


FREE WHITE PAPER
Discover our in-depth analysis of the concept of employee engagement, its roots, and ways to improve it significantly
Ever spent 20 minutes searching for a project brief you knew existed? Or answered the same question for the third time this week? You’re not alone. Companies are drowning in information, and our old ways of managing it—scattered files, endless email chains, that one co-worker who knows everything—are breaking down.
Knowledge is the lifeblood of any organization. As businesses navigate the complexities of the digital age and remote work environments, the challenge of capturing, organizing, and sharing collective intelligence has become paramount.

This challenge is met by Knowledge Management Software (KMS), a critical tool for operational efficiency, innovation, and customer satisfaction. The modern Knowledge Management Software (KMS) is no longer a simple repository; it’s an intelligent, collaborative hub, fundamentally reshaping how organizations operate.
This is where Knowledge Management Software (KMS) comes in. Think of it as your organization’s collective brain: a single source of truth that captures what your team knows and makes it easy for everyone to find. With the right system, teams move faster, customers get better answers, and innovation accelerates.
But with dozens of KMS options out there, choosing the right one can feel overwhelming. The goal isn’t to find the “best” software—it’s to find the best fit for your team’s workflow and culture.
In this guide, we’ll explore the best Knowledge Management tools in 2025, highlight their key features, and provide practical insights to help you transform your team’s knowledge into a real competitive advantage.
Knowledge Management Software (KMS) is a technology solution that helps organizations capture, organize, share, and make the most of their collective knowledge. It acts like a corporate brain—a centralized hub where employees can access company policies, project documentation, best practices, technical specifications, FAQs, and other critical information.
A modern Knowledge Management Software (KMS) often includes knowledge bases, wikis, document repositories, enterprise search, Q&A systems, collaboration spaces, and increasingly AI-powered features such as semantic search, automated summarization, and content recommendations. By turning “tribal knowledge” (the insights that live in people’s heads or scattered documents) into structured, reusable assets, KMS ensures that the right information reaches the right person at the right time.
Organizations use Knowledge Management Software (KMS) to support customer service, onboarding, compliance, research and development, and everyday workflow efficiency. As businesses adopt cloud solutions and generative AI, the knowledge management market is rapidly evolving, making these tools more intelligent, collaborative, and essential than ever.
Knowledge management tools are often confused with other types of software. Understanding the differences can help you pick the right solution for your organization. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Tool / System | Focus | Typical Use Case | Pros | Cons |
| Knowledge Base (KB) | Structured information repository | FAQs, guides, troubleshooting for employees or customers | Quick access to key knowledge, reduces repetitive questions, core KM component | Can become outdated without maintenance, limited collaboration features |
| Intranet / Digital Workplace | Centralized hub for news, tools, collaboration, and culture | Company-wide communication, collaboration, hosting KM systems | All-in-one platform, enhances collaboration, can embed KM | Broader scope may dilute focus on deep knowledge management |
| Document Management System (DMS) | File storage, version control, compliance | Legal docs, contracts, HR or regulated documents | Ensures compliance, secure file management | Less focus on discoverability, limited knowledge-sharing features |
| Learning Management System (LMS) | Training and structured learning | Employee onboarding, skill development, certification programs | Delivers curated knowledge, tracks progress | Focused on learning, not knowledge capture or discovery |
| Enterprise Search / Indexing | Search and discovery across systems | Locating policies, project documents, expertise | Connects multiple knowledge sources, supports semantic and AI search | Relies on underlying systems being well-organized, can be complex to set up |
Knowledge Management Software (KMS) comes in many forms, each tailored to different needs, audiences, and organizational goals. No single tool fits every use case—some focus on customer-facing knowledge, others on internal collaboration or AI-powered discovery.
Below is a guide to the main types of Knowledge Management Software and what makes each one unique.
Enterprise wikis are collaborative spaces where employees can document and update knowledge collectively. They’re ideal for maintaining internal policies, procedures, and step-by-step guides that evolve over time.
Knowledge bases are structured repositories of articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides, optimized for search and easy navigation. They serve both internal and external audiences—employees seeking answers or customers using self-service support portals.
These platforms center on conversation and peer-to-peer learning. Users ask questions, share expertise, and collaborate through threaded discussions or forums. Communities can be internal (for employees) or external (for customers and partners).
A DMS focuses on storing and governing files securely while maintaining compliance and version control. It’s especially valuable for industries that handle large volumes of regulated documents, such as legal, finance, or healthcare.
These platforms act as intelligent search engines that connect all organizational data—documents, chat messages, wikis, CRM records—and make it instantly retrievable through semantic or vector search. They are often layered over multiple systems to provide unified access to knowledge.
AI assistants and chatbots represent the newest frontier in Knowledge Management. These tools sit on top of existing knowledge systems to synthesize, summarize, and deliver answers in real time.
Digital workplace suites combine knowledge management with communication, collaboration, and social engagement features. These integrated platforms serve as a company’s digital hub—where teams work, share, and learn together.

The Complete Guide to
Employee Engagement
Discover our in-depth analysis of the concept of employee engagement, its roots, and ways to improve it significantly



Discover our in-depth analysis of the concept of employee engagement, its roots, and ways to improve it significantly
Selecting the right type of Knowledge Management Software depends on your organization’s size, structure, and goals.
In many cases, the most effective approach is a combination of these tools—integrating structured documentation, social collaboration, and intelligent search within a single digital ecosystem.
| KMS Type | Primary Focus | Key Features | Typical Use Case | Examples |
| Customer-Facing Knowledge Base / Help Center | External customer support and self-service | Public knowledge base, FAQs, decision trees, AI chatbots, analytics | Online support centers, customer portals, product documentation | Zendesk Guide, Freshdesk, Helpjuice |
| Enterprise Wiki / Intranet | Internal collaboration and knowledge retention | Editable wiki pages, enterprise search, employee profiles, version control, social features (comments, feeds) | Internal documentation, HR policy centralization, process manuals, onboarding resources | Confluence, Notion, Slite, eXo Platform |
| Integrated Digital Workplace Suite | Unified collaboration, communication, and knowledge sharing | Intranet, document management, project spaces, social networking, enterprise search, gamification | Building a connected digital workplace or corporate intranet | eXo Platform, Microsoft Viva, LumApps |
| Document Repository / DMS | Secure document storage, version control, and compliance | Metadata tagging, retention rules, audit trails, access controls | Legal and HR document storage, compliance archives, contract management | SharePoint, M-Files, DocuWare |
| Community & Q&A Platform | Peer-to-peer knowledge exchange and expert collaboration | Discussion threads, Q&A, user voting, moderation tools, reputation systems | Internal expert communities, customer or partner forums | Discourse, Stack Overflow for Teams, eXo Platform |
| AI-Assistant Layer | Automated knowledge discovery and conversational access | Semantic search, document summarization, contextual Q&A, chatbot integration | AI-powered employee assistants, customer support bots | ChatGPT Enterprise, Moveworks, Forethought |
| Search & Discovery Platform | Unified and intelligent knowledge retrieval | Semantic and vector search, content indexing, cross-system integration | Searching across all company tools (Drive, CRM, Slack, etc.) | Glean, Coveo, Elastic Enterprise Search |
| Learning Management System (LMS) | Structured training and learning delivery | Course creation, certification tracking, progress analytics, microlearning | Employee onboarding, upskilling, training programs | Docebo, Cornerstone, TalentLMS |
Most organizations benefit from a combination of these tools rather than relying on a single system. For instance:
A thoughtful blend of these types ensures knowledge flows seamlessly — across teams, systems, and customer touchpoints — making it discoverable, actionable, and future-proof.
Knowledge Management Software (KMS) delivers measurable, organization-wide impact. Beyond simply storing information, a well-implemented KMS improves productivity, speeds up problem-solving, preserves expertise, and fosters a more connected and innovative workplace.
Let’s explore the key benefits and outcomes businesses can expect when adopting a robust knowledge management strategy.
When knowledge is scattered across emails, folders, and personal notes, employees waste valuable time searching for answers or recreating existing work. KMS centralizes information, making it quick and easy to find verified content.
For customer-facing teams, access to a well-maintained knowledge base or AI-assisted help center means faster answers and fewer errors. Agents no longer need to consult multiple sources or escalate simple issues.
New employees often struggle to locate key resources or understand company procedures. A Knowledge Management Software (KMS) acts as an onboarding companion—centralizing everything from policies to training materials.
When experienced employees retire or move on, their knowledge often leaves with them. Knowledge Management Software captures this institutional wisdom—documenting processes, lessons learned, and best practices for future use.
A Knowledge Management Software (KMS) creates a shared space where teams contribute to and refine collective knowledge. It breaks down silos between departments and promotes transparency.
By centralizing policies, guidelines, and templates, Knowledge Management Software (KMS) ensures that everyone follows the same procedures. This is especially critical for regulated sectors like healthcare, finance, or government.
When employees have easy access to the knowledge they need, they feel empowered and supported. A Knowledge Management Software (KMS) fosters transparency and encourages continuous learning, collaboration, and contribution.
Knowledge doesn’t just support daily operations—it drives innovation. By making lessons learned, R&D insights, and historical data easily accessible, a Knowledge Management Software (KMS) enables teams to build upon past successes and avoid repeated mistakes.
The financial impact of effective knowledge management is well-documented. Organizations that implement Knowledge Management Software (KMS) solutions report measurable ROI through lower training costs, reduced support workloads, and faster time-to-market.
| Category | Key Benefit | Impact |
| Efficiency | Increased employee productivity | Employees find information faster and avoid duplicated work. |
| Financial | Reduced operational costs | Lower training expenses, fewer support tickets, faster time-to-market. |
| Quality & Risk | Improved consistency and accuracy | Ensures all stakeholders follow a single source of truth, reducing errors and supporting compliance. |
| Human Capital | Faster onboarding and training | New hires become productive quickly with guided resources. |
| Culture | Fostering collaboration and innovation | Encourages cross-team sharing and idea generation, leading to continuous improvement. |
A strong Knowledge Management Software solution delivers far more than convenience—it creates measurable business value. It cuts costs, saves time, empowers employees, and ensures critical knowledge is preserved and leveraged. Whether your goal is faster onboarding, better customer support, or sustained innovation, the right Knowledge Management system becomes a strategic advantage—turning information into insight and insight into action.n
The landscape of Knowledge Management Software (KMS) has transformed dramatically in recent years. What used to be static repositories for documents and FAQs have evolved into intelligent, connected, and AI-driven ecosystems that actively support daily work, collaboration, and decision-making.
As organizations enter 2025, modern KMS platforms are no longer “nice-to-have” tools—they are strategic enablers of productivity, innovation, and competitive agility. Below, we explore the key features and trends that define the new generation of Knowledge Management Software and what you should prioritize when selecting your next platform.
Artificial Intelligence is at the heart of today’s KM revolution. Modern systems leverage AI not just to improve search, but to actively curate, generate, and recommend knowledge.
Why it matters: Employees spend less time searching and more time acting on accurate, contextual knowledge—driving measurable productivity gains.
In 2025, knowledge management doesn’t happen in isolation. The best KMS tools are deeply integrated into the apps teams already use.
API-first architectures and universal search functions make it possible to pull data from emails, shared drives, ticketing systems, meeting transcripts, and more—all searchable from one interface.
Why it matters: Knowledge becomes instantly accessible across your ecosystem, eliminating data silos and ensuring that employees never have to “switch context” to find answers.
The most valuable knowledge often lives inside people’s heads. That’s why modern KMS platforms go beyond documentation—they create vibrant spaces for collaboration and tacit knowledge exchange.
Why it matters: A collaborative KMS builds a living, breathing culture of learning and innovation—transforming knowledge management from a static library into a social experience.
As knowledge bases expand, managing their accuracy and relevance becomes critical. Modern systems incorporate governance frameworks that maintain content quality and compliance.
Why it matters: These tools prevent information overload, reduce risk, and ensure that users always access verified, up-to-date knowledge.
Large organizations often need to manage knowledge for multiple audiences—internal teams, partners, and customers.
Why it matters: Flexible architecture ensures clarity, consistency, and personalization for every audience segment.
In 2025, data-driven knowledge management is essential. The best platforms include deep analytics that help organizations continuously optimize their content and processes.
Why it matters: Analytics transform Knowledge Management from a passive repository into an active intelligence system that evolves with organizational needs.
With remote and hybrid work now standard, employees need access to knowledge anytime, anywhere, and on any device.
Why it matters: Knowledge remains at employees’ fingertips—whether they’re in the office, at home, or on the move.
AI isn’t just enhancing search—it’s automating the upkeep of entire knowledge ecosystems.
Why it matters: These automations save administrators hours of manual maintenance and keep the knowledge base fresh, relevant, and self-improving.
As data privacy regulations grow stricter, enterprises demand strong security foundations in their Knowledge Management platforms.
Why it matters: Trust and compliance are non-negotiable when managing an organization’s collective intelligence.
| Feature Category | Description | Impact |
| AI & Search Intelligence | Semantic and generative AI enable contextual, conversational results. | Faster and more accurate access to knowledge. |
| Integrations & API-first Design | Connects with CRMs, ticketing, and collaboration tools. | Unified access and reduced information silos. |
| Collaboration Tools | Co-authoring, discussions, gamification, and feedback loops. | Encourages active knowledge sharing and participation. |
| Governance & Compliance | Review cycles, versioning, retention, and permissions. | Ensures accuracy, reliability, and compliance. |
| Analytics & Reporting | Dashboards for usage, ROI, and content gaps. | Continuous improvement and measurable impact. |
| Automation & Maintenance | AI-powered upkeep and content suggestions. | Keeps content fresh with minimal manual effort. |
| Security & Privacy | SSO, encryption, and regional hosting options. | Protects data and builds user trust. |
| Mobility & Accessibility | Seamless multi-device access for all users. | Supports remote and hybrid teams globally. |
The Knowledge Management Software of 2025 is intelligent, integrated, and indispensable. With AI at its core and usability at its heart, it transforms how teams capture, share, and act on information. From smarter search to real-time collaboration and predictive insights, today’s Knowledge Management Software (KMS) is the foundation of a truly connected and high-performing digital workplace.
Efficient knowledge management (KM) is essential for modern organizations. The right tool helps teams capture, organize, and share knowledge, improving productivity, collaboration, and customer satisfaction. Below is a detailed overview of the top 30 KM tools in 2025, focusing on real-world use cases, strengths, and unique features. Pricing is summarized in the comparison table at the end.
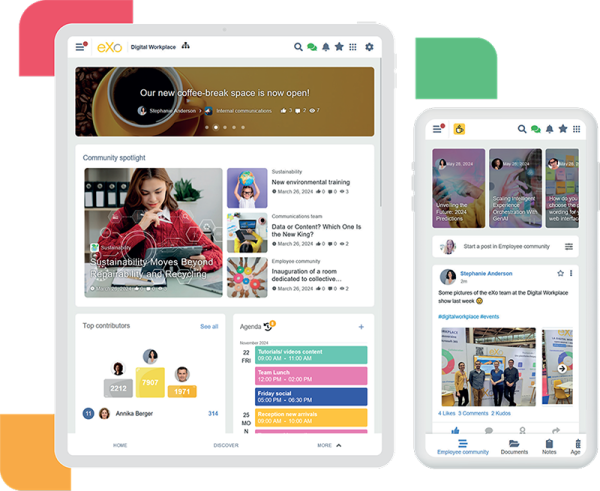
eXo Platform is far more than just a Knowledge Management (KM) tool — it’s a complete digital workplace solution built to empower medium-to-large organizations with a unified environment for collaboration, communication, and knowledge sharing.
Unlike traditional KM systems that focus solely on storing and retrieving information, eXo takes a more holistic approach. It blends knowledge management, intranet capabilities, social collaboration, and employee engagement tools into one seamless platform. This powerful combination helps organizations not only manage their collective intelligence but also nurture a strong company culture where collaboration and knowledge sharing become part of everyday work life.
At its core, eXo Platform integrates key components that most businesses typically rely on separate tools for — including a wiki, knowledge base, document management, social networking spaces, and recognition features. This means teams can co-create, document, and access knowledge while staying connected through discussions, activity streams, and internal communities.
What sets eXo apart is how it transforms static documentation into living knowledge ecosystems. Through its intuitive interface and built-in social features, employees can easily share insights, ask questions, and highlight valuable contributions. Gamification tools such as badges, points, and recognition programs keep employees engaged and motivated to contribute. These elements make knowledge sharing feel less like a chore and more like a natural, rewarding part of work.
Beyond structured documentation, eXo excels at capturing tacit knowledge — the know-how, expertise, and experience often hidden in conversations or confined to individuals. Its AI-powered expertise locator intelligently maps skills and connects employees to the right subject matter experts, ensuring that knowledge flows freely across departments and hierarchies.
From a technical perspective, eXo Platform offers flexibility and control. It can be deployed either on-premise or in the cloud, making it suitable for organizations with specific IT governance or data compliance requirements. The platform also includes robust governance features such as version control, access rights management, and multi-knowledge base (multi-KB) support to ensure security, traceability, and content accuracy.
Ultimately, eXo Platform stands out for its ability to bring together people, processes, and knowledge into a single digital environment. It helps organizations reduce tool fragmentation, streamline collaboration, and build a culture of transparency and engagement. Whether used to manage internal documentation, facilitate cross-team projects, or foster a connected corporate community, eXo delivers the structure, intelligence, and social layer modern enterprises need to thrive.
In short, eXo Platform is not just a tool — it’s a workplace ecosystem. It’s designed for companies that want to go beyond simple knowledge storage and instead build a dynamic, connected, and knowledge-driven organization.
eXo Platform brings together an impressive set of features that go far beyond traditional knowledge management tools. It’s built to centralize collaboration, enhance employee engagement, and simplify information governance — all within one cohesive digital environment. Below are the key advantages that make eXo stand out as an all-in-one workplace solution:
One of eXo’s biggest strengths is its ability to replace multiple separate tools with a single, integrated platform. Instead of juggling between a wiki for documentation, a chat app for discussions, a social network for updates, and an intranet for communication, eXo brings everything together under one roof.
This integration not only reduces tool sprawl and costs but also creates a more seamless user experience. Employees can share documents, collaborate in real time, comment on posts, and access organizational knowledge — all without switching between systems. The result is improved efficiency, fewer silos, and a more connected digital ecosystem.
Features such as activity streams, collaborative spaces, and discussion threads allow employees to connect around topics and projects. Gamification elements like badges, points, and leaderboards reward participation and make contributions visible and valued. On top of that, employee recognition tools help managers and peers celebrate achievements, fostering a culture of appreciation and continuous learning.
This focus on engagement turns what could be a static KM system into a dynamic and living knowledge community.
Every organization has different IT needs, and eXo offers true deployment flexibility to accommodate them. Companies can choose between cloud-based deployment for convenience and scalability or on-premise hosting for greater control, customization, and data sovereignty.
This flexibility makes eXo suitable for both highly regulated industries that require strict compliance and modern enterprises seeking cloud agility. In either case, organizations maintain full control over their infrastructure, integrations, and user management.
eXo was built with enterprise governance in mind. The platform includes advanced versioning, access controls, and content lifecycle policies that maintain the integrity and accuracy of information.
Administrators can define who can create, edit, or publish content, ensuring compliance with internal and external standards. The multi-knowledge base (multi-KB) architecture also allows organizations to manage different repositories for different teams or business units, while still maintaining unified search and analytics.
Combined with strong data security and audit capabilities, these features make eXo a trusted choice for enterprise-scale knowledge management.
eXo Platform is purpose-built for medium-to-large enterprises that manage complex organizational structures, multiple departments, and significant volumes of knowledge. This focus means it provides extensive functionality, customization, and governance capabilities — but these can also make it overly robust for small teams or startups.
Smaller organizations may find that they only use a fraction of eXo’s potential, making it feel heavier or more feature-rich than necessary for their scale. For such teams, lighter, plug-and-play KM tools might deliver faster value with less setup. However, for larger companies with established workflows and the need for integrated collaboration, eXo’s breadth becomes a major advantage.
Because of its comprehensive nature, implementing eXo Platform typically involves careful planning, configuration, and change management. Unlike simple SaaS KM tools that can be deployed instantly, eXo’s setup may require dedicated IT involvement and a well-defined adoption strategy to get the most out of its modules.
Organizations need to configure spaces, permissions, content structures, and integrations to align with their internal workflows. This investment pays off in the long run — as it enables a tailored, scalable environment — but it does mean that deployment can take longer compared to lighter tools.
In short, eXo is a platform meant to be built around an organization’s culture and processes, not just installed and forgotten.
Another important consideration is that eXo Platform is primarily designed for internal collaboration and knowledge sharing rather than public-facing knowledge bases. Its strength lies in connecting employees, departments, and communities within the organization.
While it can technically host external spaces or partner portals, it’s not optimized for open access documentation or customer self-service knowledge bases in the way that tools like Zendesk or Helpjuice are. For companies seeking to manage both internal and external knowledge experiences, eXo may need to be paired with a customer-facing solution.
As an enterprise-grade platform, eXo’s pricing model reflects its scope, flexibility, and deployment options. Costs can vary based on the number of users, hosting preference (cloud or on-premise), and required modules or support levels. While pricing is provided upon request, it’s generally positioned at the enterprise investment level, which might exceed the budget of smaller organizations.
That said, eXo’s value lies in its ability to replace multiple systems, potentially reducing overall software costs and complexity over time.
For organizations looking to unify knowledge management, social collaboration, intranet functions, and employee engagement under a single platform, eXo Platform provides a powerful, flexible, and scalable solution. By bridging knowledge sharing with culture-building features, it transforms KM from a static repository into an active, participatory workplace experience.
In summary, while eXo Platform shines as a robust, all-in-one digital workplace, it’s best suited for organizations that have the scale, resources, and strategic vision to leverage its full potential. For those who invest in proper implementation and adoption, the platform delivers a rich, long-term foundation for collaboration and knowledge-driven culture.

Types of Digital workplace solutions
Digital workplace is a buzzword these days. Actually different people use it to mean different things. So what is a digital workplace?



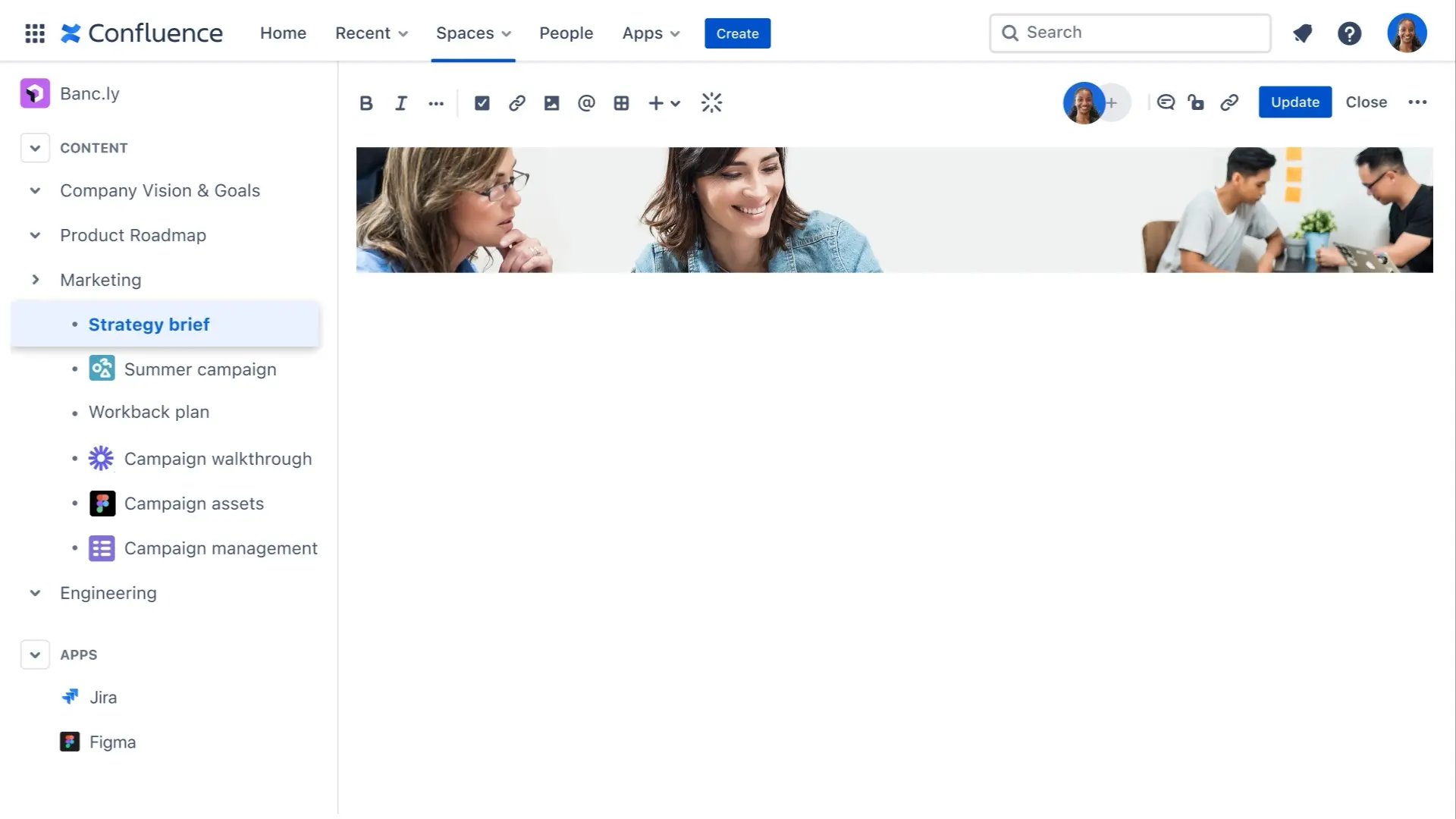
Confluence by Atlassian is one of the most recognized and widely used knowledge management and documentation platforms in the enterprise world. Originally designed as a corporate wiki, Confluence excels at helping teams create, organize, and manage structured documentation at scale.
It’s particularly powerful for organizations already invested in the Atlassian ecosystem — especially those using Jira, Trello, or Bitbucket. The native integrations between these tools make it easy to link project documentation, technical specs, sprint retrospectives, and product requirements directly within Confluence pages. This seamless connection between documentation and project execution allows teams to maintain transparency, traceability, and alignment throughout the development lifecycle.
Confluence is structured around a system of pages and spaces, where each space can represent a team, department, or project. This hierarchy helps maintain order even in large organizations managing thousands of pages. Pre-built templates for meeting notes, product roadmaps, project briefs, and knowledge bases also help teams get started quickly while maintaining consistency across content.
Additionally, the Atlassian Marketplace offers hundreds of add-ons and integrations — from advanced analytics to visual diagram tools — allowing companies to tailor the platform to their exact needs. For IT, HR, and product teams that value organization, structure, and cross-functional collaboration, Confluence is often seen as the industry standard for internal documentation.
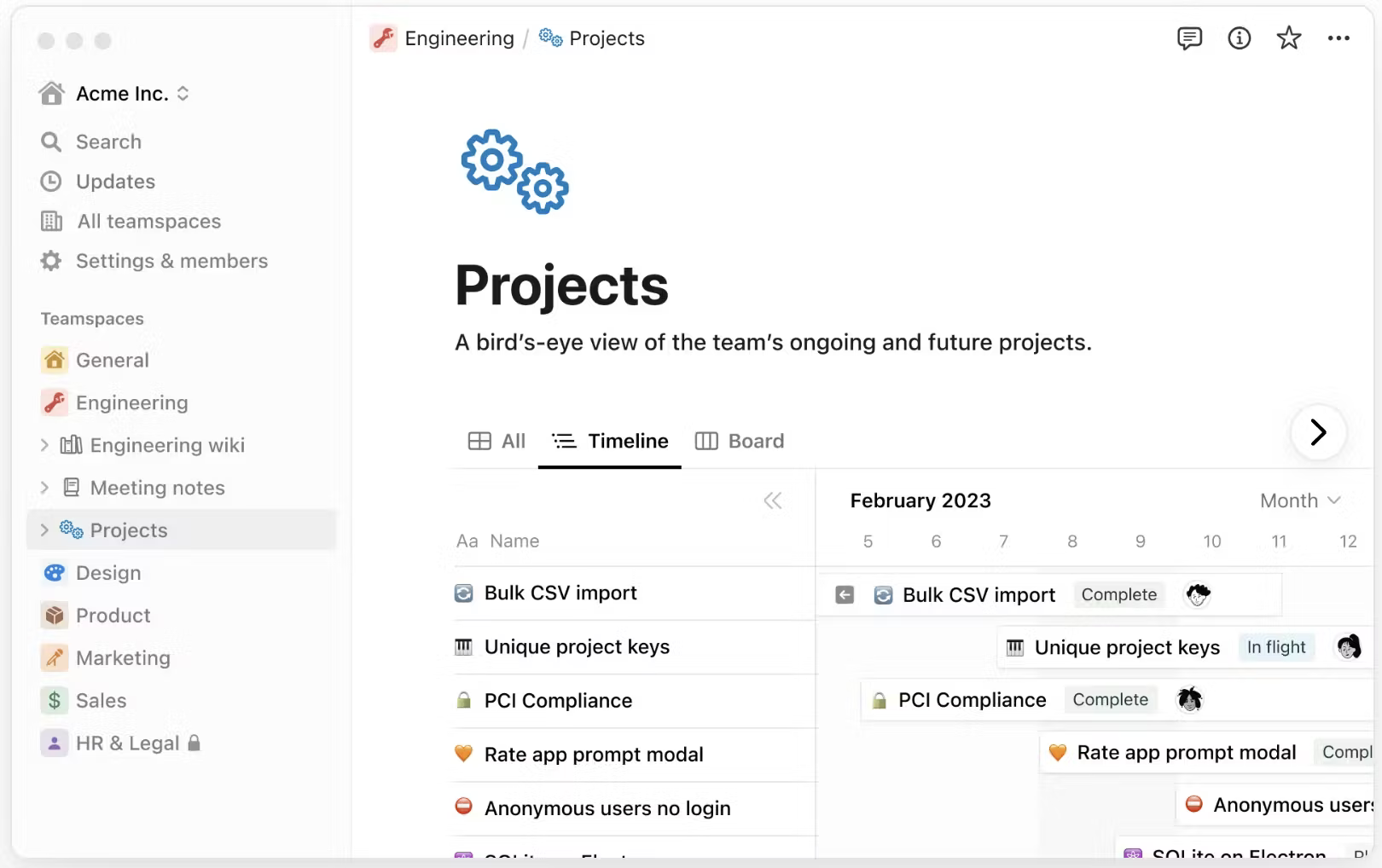
Notion has become one of the most popular tools for modern teams — and for good reason. Often described as a digital Lego set, Notion gives users the power to build exactly what they need, whether that’s a simple note-taking hub, a company wiki, a task tracker, or a full-fledged project management workspace.
Unlike traditional knowledge management tools that enforce rigid structures, Notion offers extreme flexibility. It combines notes, documents, wikis, databases, and project boards in a clean, minimalist interface. Everything is modular — users can start with a blank page and add text, tables, checklists, embeds, and more, creating fully customized pages and dashboards tailored to their workflow.
This flexibility makes Notion especially appealing for startups, small teams, and creative organizations that value autonomy and agility. Its interface is visually intuitive and beautifully designed, allowing users to organize content in a way that feels natural and engaging. Teams can collaborate on shared pages, comment inline, and use databases to track projects, goals, or documentation — all without the complexity of heavier enterprise systems.
Notion also shines in its simplicity and accessibility. Individuals and small teams can get started quickly using the generous free plan, while larger teams can scale up with paid tiers offering advanced permissions and admin controls. The tool’s growing ecosystem of community-built templates makes it easy to launch common setups like company handbooks, product roadmaps, or client portals in minutes.
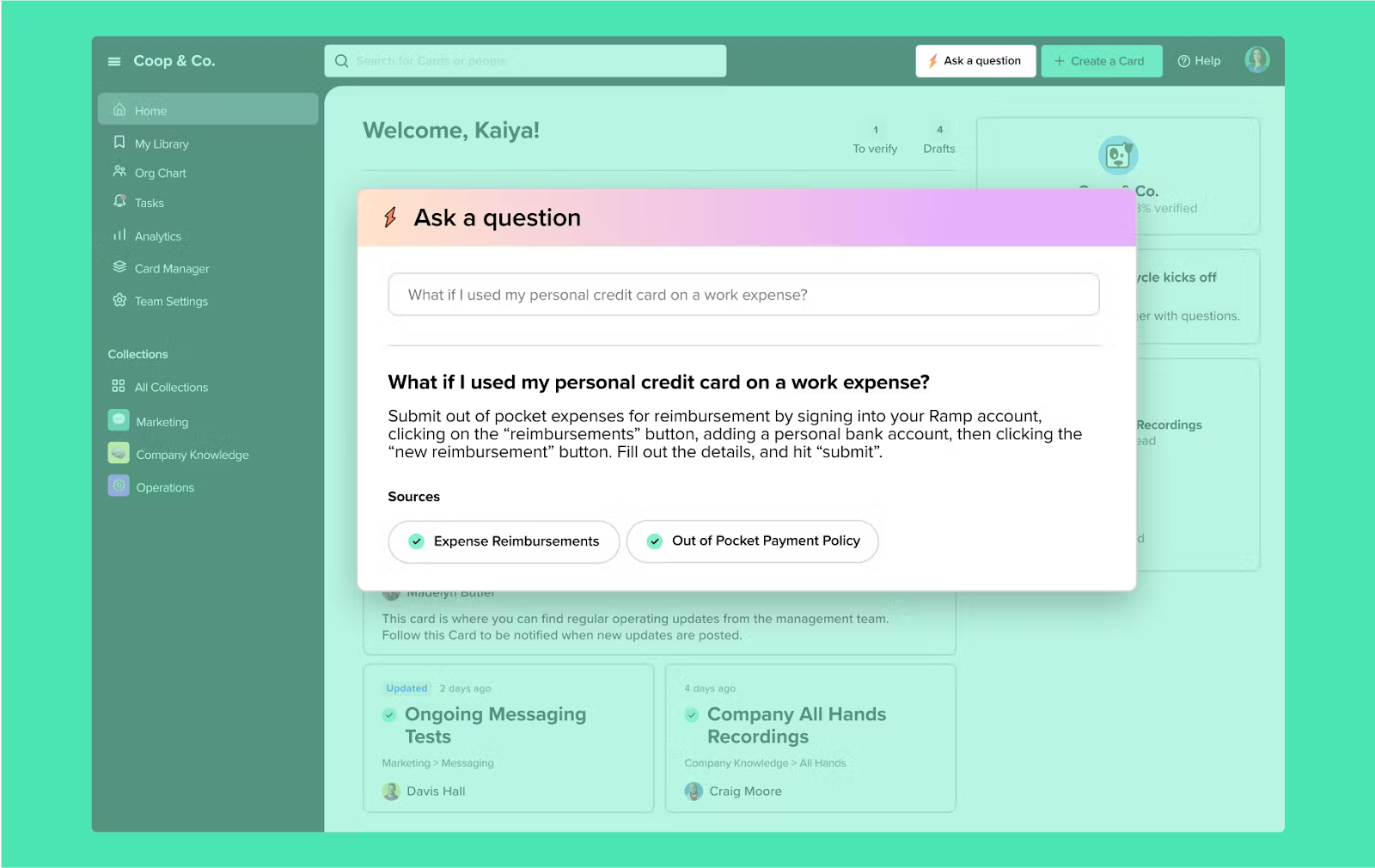
Guru takes a unique approach to knowledge management by focusing on knowledge delivery at the point of need rather than expecting employees to search for it in a separate platform. Instead of acting as a standalone wiki or database, Guru integrates directly into the tools your teams already use — such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, Chrome, and Salesforce — ensuring that verified information is just a click away in daily workflows.
At its core, Guru is built around “Cards” — compact, structured units of information that capture key answers, processes, or reference materials. Each Card can be verified by subject matter experts (SMEs), keeping the content accurate and trustworthy. This verification process, assisted by AI reminders, helps prevent outdated or redundant information from circulating — a common challenge in growing organizations.
Guru is particularly strong for customer-facing, sales, and support teams, where quick, contextual access to accurate information directly impacts performance and response quality. It reduces context switching — employees don’t have to leave their chat or CRM window to find the right answer. The Chrome extension and Slack bot make it possible to access and share Cards instantly during live interactions.
While Guru isn’t designed for long-form documentation or complex hierarchical knowledge bases, it excels in knowledge enablement — helping teams make better decisions faster by bringing verified knowledge into the flow of work.
Microsoft SharePoint is a powerful, enterprise-focused platform designed for organizations that manage large volumes of documents and are already invested in the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. It combines enterprise-grade document management, internal knowledge hubs, and intranet portals in a single platform. SharePoint excels at providing structured workflows, governance, and secure access to critical organizational information, making it particularly valuable for large teams and regulated industries.
One of SharePoint’s key strengths is its deep integration with Microsoft Office apps, such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Teams. This allows employees to seamlessly edit, co-author, and share documents without leaving familiar Microsoft interfaces. SharePoint also supports versioning, content approval workflows, metadata, and custom permission controls, ensuring that sensitive information is managed with precision and compliance requirements are met.
SharePoint is highly flexible and can serve as both a central knowledge repository and a company intranet, providing news feeds, portals, team sites, and dashboards that keep employees informed and aligned. Its extensive customization options and third-party integrations allow organizations to tailor SharePoint to their unique workflows, from HR onboarding to project documentation and internal wikis.

Open Source Alternative to Microsoft 365
Empower your organization with eXo Platform to break free from Microsoft dependencies and enhance collaboration with innovative solutions
Open Source Alternative to Microsoft 365
Empower your organization with eXo Platform to break free from Microsoft dependencies and enhance collaboration with innovative solutions

Bitrix24 is a comprehensive collaboration platform that brings together team communication, project management, intranet capabilities, and a knowledge base in a single environment. Designed with budget-conscious teams and small-to-medium businesses in mind, it allows organizations to manage multiple collaboration needs without subscribing to multiple tools.
The platform includes chat, video calls, task management, document sharing, CRM, and workflow automation, all integrated with a knowledge base module. While the KM features are not as advanced or specialized as those in dedicated knowledge management systems, they provide a functional solution for teams that want to store, organize, and share internal information alongside their collaboration tools.
Bitrix24 is particularly attractive for organizations seeking an all-in-one suite at minimal cost. Its free tier makes it accessible for small teams, startups, or companies experimenting with digital workplace tools before committing to a paid plan.
Bloomfire is a socially-driven knowledge management platform designed to make knowledge discovery and sharing both easy and engaging. Unlike traditional, document-heavy KM tools, Bloomfire emphasizes content feeds, Q&A interactions, and collaborative learning, creating an environment where employees can quickly find, share, and discuss knowledge.
The platform leverages AI-enabled search to surface relevant content based on keywords, topics, and user behavior. This makes it especially useful for distributed teams or organizations with large, dynamic workforces, where finding the right information quickly is critical. Bloomfire’s interface is user-friendly and designed to feel familiar to anyone accustomed to social media feeds, encouraging participation and adoption across teams.
Bloomfire is ideal for organizations that want to foster engagement and knowledge sharing rather than just store documents. Its emphasis on social collaboration and content discovery helps employees interact with knowledge in real time, creating a more active and connected learning culture.
Document360 is a documentation-first knowledge management platform designed to provide structured, organized, and easily navigable content for both internal teams and external users. It is particularly well-suited for product teams, customer support departments, and companies that need customer-facing self-service portals.
The platform emphasizes clarity and organization, supporting article categorization, robust version control, and granular role-based permissions. This makes it easy for teams to maintain consistent, up-to-date documentation, track changes, and control access at multiple levels. Its structured approach ensures that knowledge is not just stored but well-governed and discoverable, reducing confusion and information gaps.
While Document360 shines as a dedicated knowledge base solution, it is less focused on social or collaborative aspects. Unlike platforms like Bloomfire or Guru, it does not emphasize real-time engagement, feed-based knowledge discovery, or chat-based collaboration. Instead, its strength lies in creating reliable, maintainable, and professional documentation that can serve both internal employees and external customers.
Zendesk Guide is a knowledge management platform tailored for customer support teams, designed to provide both internal and external knowledge solutions. It allows organizations to create internal agent-focused knowledge bases as well as public-facing help centers, ensuring that both employees and customers can quickly access accurate, actionable information.
Tightly integrated with the Zendesk Suite, Guide connects knowledge articles directly to support tickets, enabling agents to reference solutions efficiently while responding to inquiries. This integration not only improves ticket resolution times but also reduces duplicate tickets by empowering customers to find answers independently through self-service portals.
While Document360 shines as a dedicated knowledge base solution, it is less focused on social or collaborative aspects. Unlike platforms like Bloomfire or Guru, it does not emphasize real-time engagement, feed-based knowledge discovery, or chat-based collaboration. Instead, its strength lies in creating reliable, maintainable, and professional documentation that can serve both internal employees and external customers.
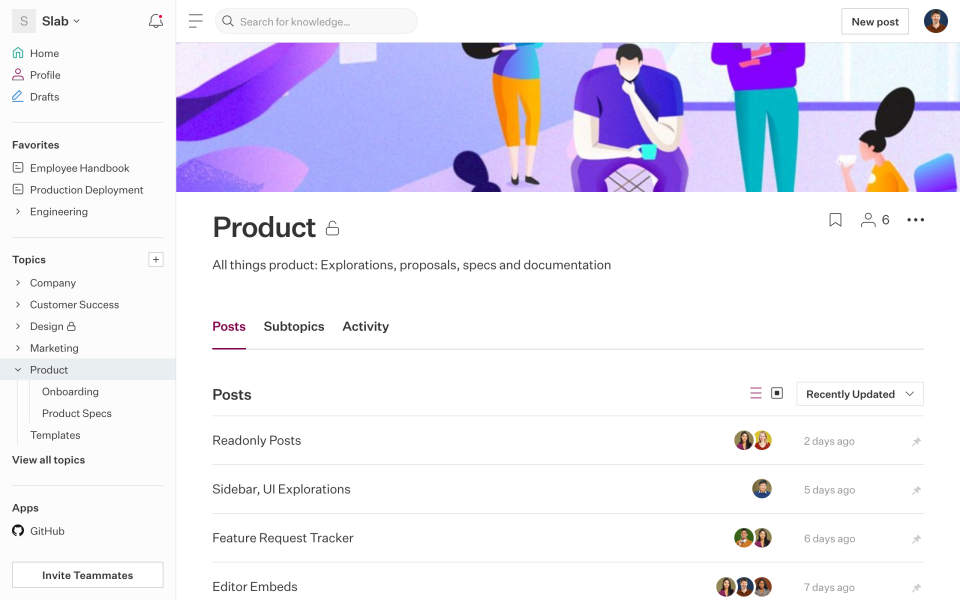
Slab is a lightweight, user-friendly knowledge management platform designed to make capturing, organizing, and sharing knowledge fast and intuitive. Its clean, visually appealing interface emphasizes speed and simplicity, helping teams focus on creating and finding content without unnecessary complexity.
The platform integrates seamlessly with popular collaboration tools such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Google Drive, allowing knowledge to flow naturally within existing workflows. Slab is particularly effective for teams looking for a centralized internal wiki, where documents, guides, and best practices can be stored in a structured, easily searchable way.
Unlike more flexible all-in-one platforms like Notion, Slab is optimized for internal knowledge management rather than external or customer-facing documentation. It emphasizes clarity, discoverability, and fast access to critical information, making it a strong choice for teams that prioritize efficiency and collaboration over customization.
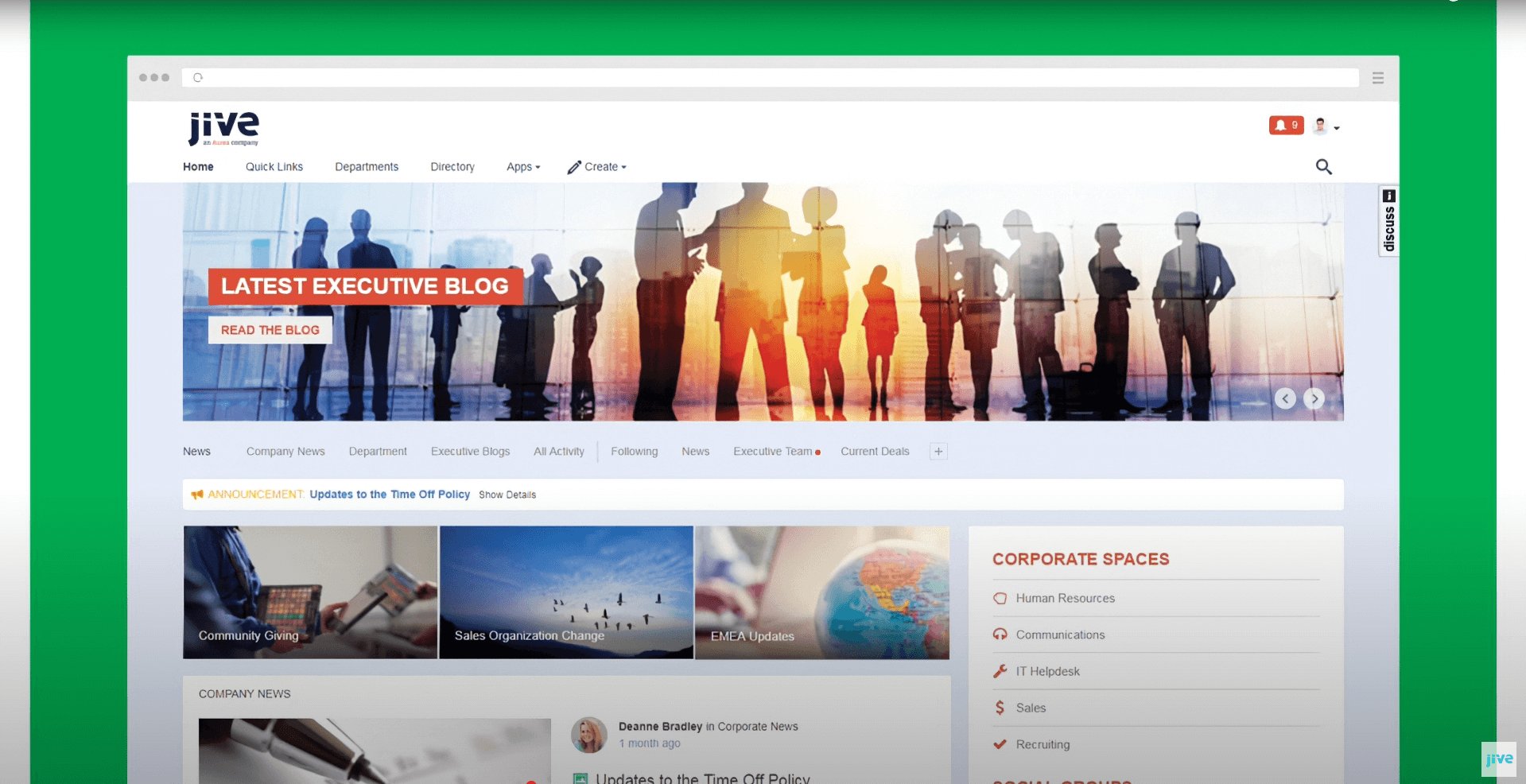
Jive, now part of Aurea, is a mature enterprise collaboration platform that combines social networking features with robust knowledge management capabilities. It is designed to help large organizations foster engagement, collaboration, and knowledge sharing across distributed teams.
Jive’s platform offers discussion forums, activity streams, communities, document libraries, and wikis, creating a social layer around organizational knowledge. Employees can easily share expertise, collaborate on projects, and discover information through community-driven content. This approach not only captures explicit knowledge in documents but also tacit knowledge embedded in conversations and social interactions.
Jive is particularly strong for enterprises that value employee engagement and community-building alongside knowledge management. It enables organizations to create a participatory digital workplace where learning, collaboration, and knowledge capture happen organically. Its governance tools, analytics, and integration options ensure that content remains secure, discoverable, and aligned with organizational policies.
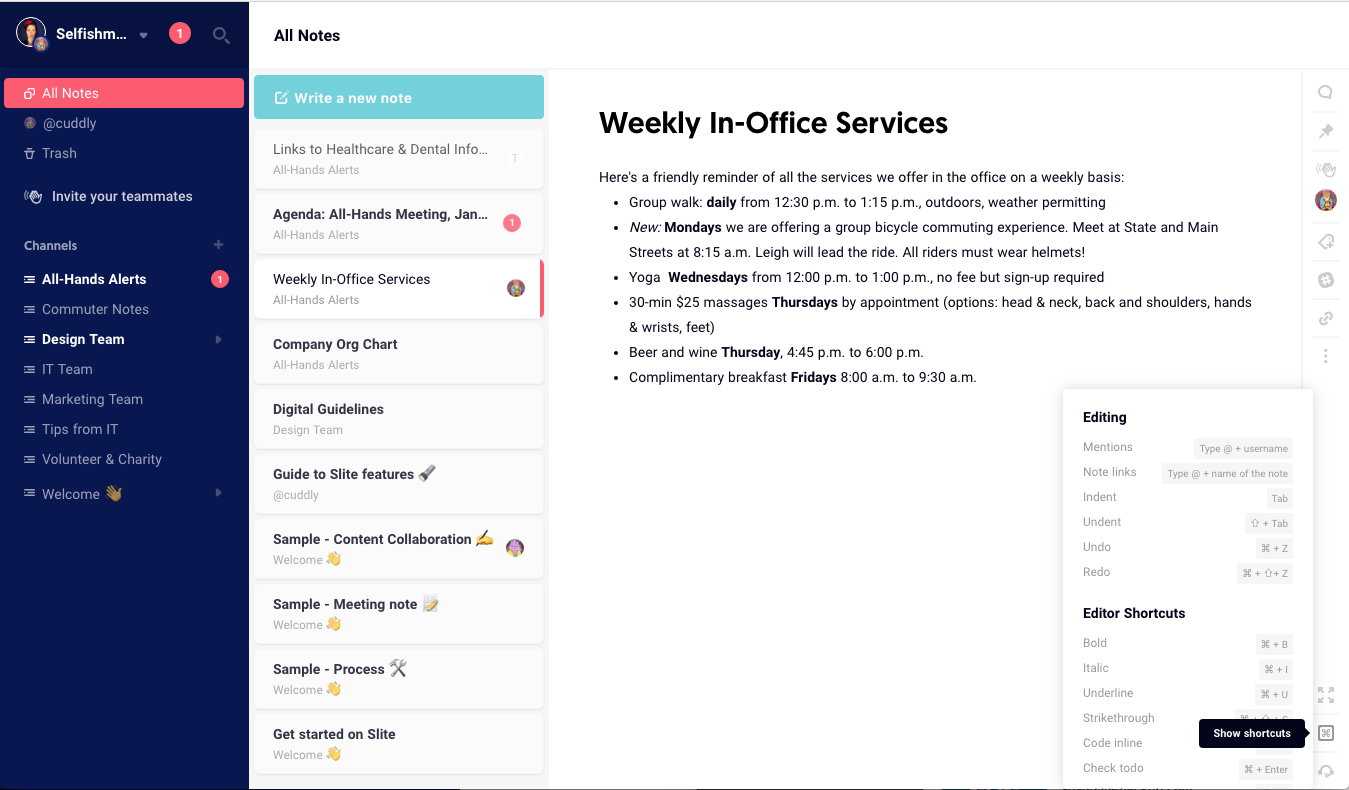
Slite is a clean, intuitive, and fast wiki platform designed for internal team knowledge. It is particularly popular with engineering teams, product managers, and small-to-medium organizations for creating runbooks, product documentation, meeting notes, and knowledge bases. Its simplicity and speed make it easy for teams to adopt without heavy onboarding or complex setup.
Slite integrates seamlessly with Slack and Google Drive, embedding knowledge into existing workflows and helping teams maintain a single source of truth. Its focus on clarity, structure, and fast content retrieval makes it an ideal solution for teams that need to capture and organize internal knowledge efficiently, without the overhead of more feature-heavy platforms.
While Slite is optimized for internal knowledge, it is less flexible than Notion in terms of custom layouts, advanced templates, or workflow automation. Its smaller ecosystem of integrations and templates may limit extensibility for larger or highly specialized teams.
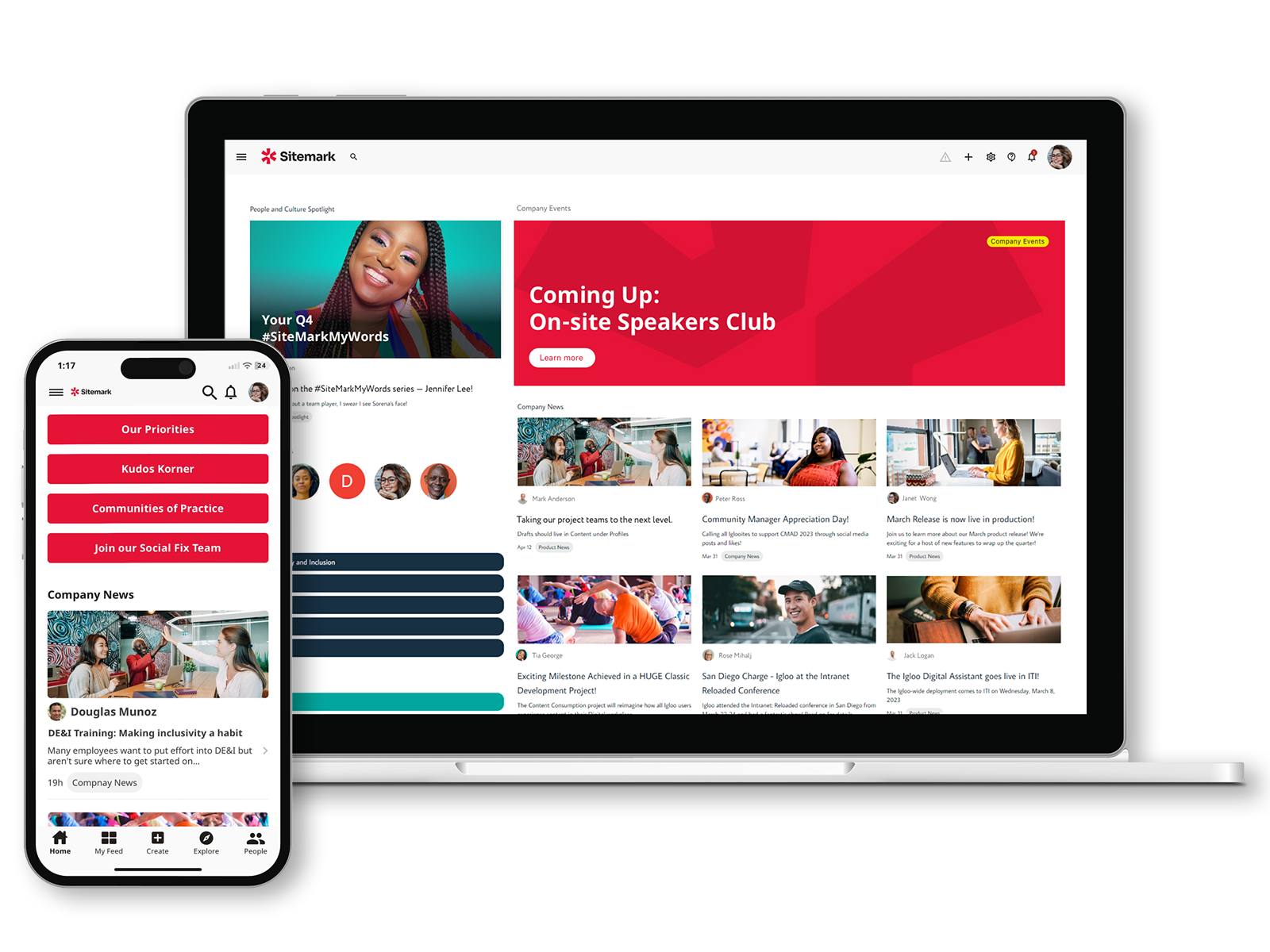
Igloo is a digital workplace platform designed to help organizations build internal communities, intranets, and knowledge hubs. Its focus is on fostering collaboration, communication, and engagement within teams, making it ideal for organizations that want to centralize content, conversations, and workflows in a single, accessible environment.
The platform allows teams to create custom intranet portals, team spaces, and community forums, enabling employees to share knowledge, updates, and resources effectively. Igloo supports content management, file sharing, and collaboration tools, ensuring that information is structured, searchable, and easy to access. Its social features, including discussion boards, activity streams, and recognition tools, encourage participation and strengthen organizational culture.
Igloo is particularly effective for medium-to-large organizations seeking to create a connected, participatory digital workplace where knowledge and collaboration coexist. While it may not have the depth of dedicated knowledge management systems, it excels in engagement-driven collaboration and community building.
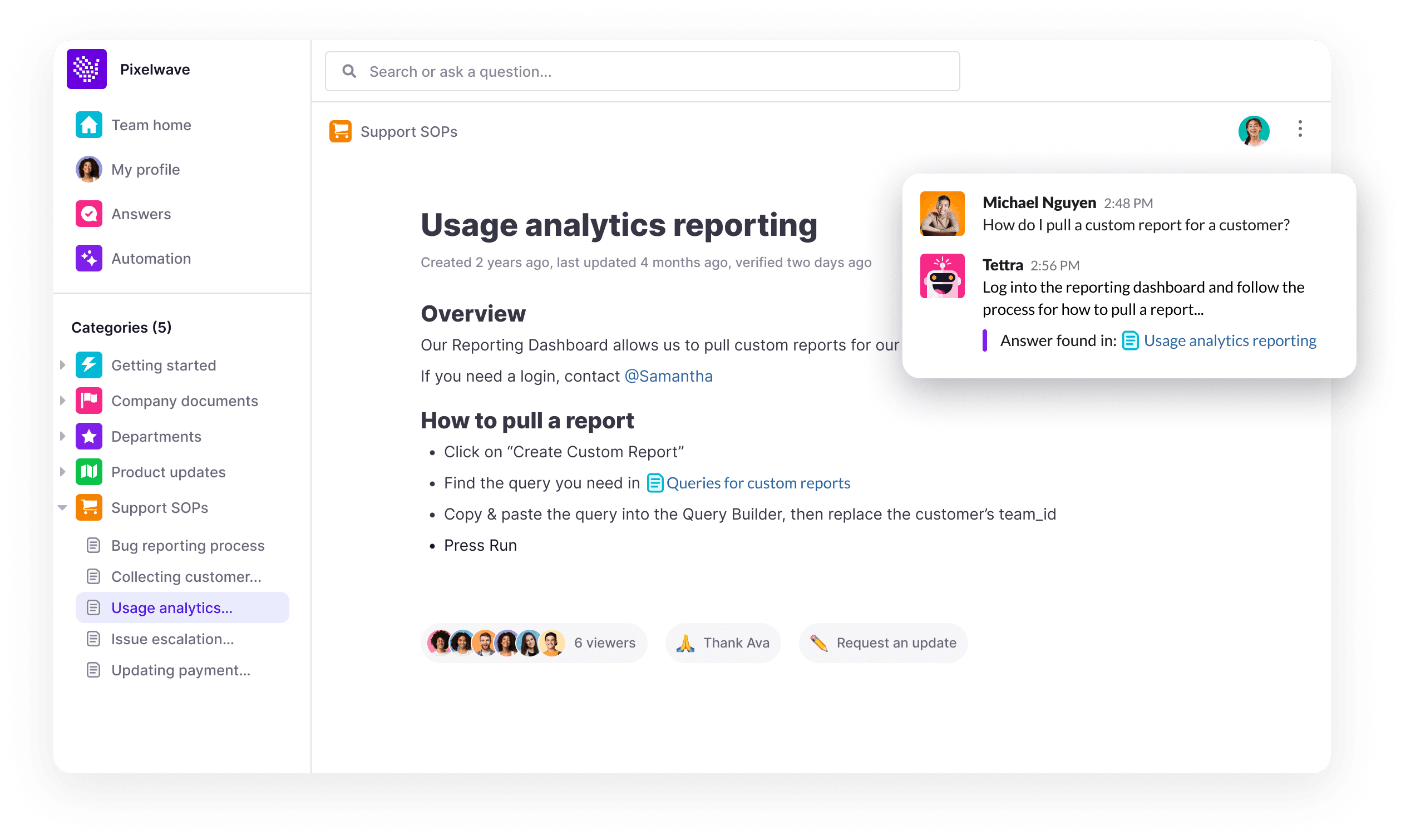
Tettra is a lightweight internal wiki designed for fast-moving teams that want to capture, organize, and share knowledge directly within Slack or Microsoft Teams. It enables employees to ask questions, find answers quickly, and contribute to a centralized internal knowledge hub without the need for a heavy intranet or complex KM platform.
Tettra’s integration with Slack and Google Workspace allows knowledge to flow naturally within existing workflows, ensuring that teams can create, update, and access content where they already collaborate. It is particularly well-suited for small-to-medium organizations or rapidly growing startups that need a simple, efficient internal knowledge system.
While Tettra excels at internal Q&A and lightweight knowledge capture, it is less suited for public-facing knowledge bases or organizations requiring robust governance, analytics, or structured documentation. Its simplicity is both a strength for adoption and a limitation for advanced KM needs.
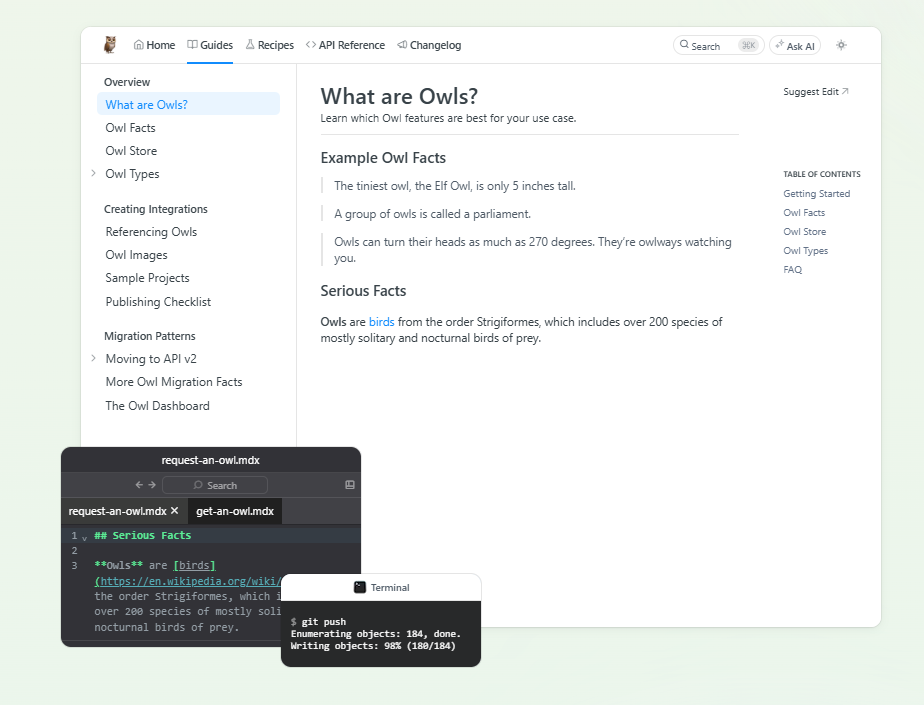
ReadMe is a developer-centric knowledge management platform designed to create interactive, versioned API documentation portals. It enables organizations to provide clear, up-to-date documentation for external developer audiences, with features like API consoles, onboarding guides, and code examples.
The platform is ideal for technology companies, SaaS providers, and API-first organizations that want to improve developer experience, reduce support queries, and provide self-service documentation for their technical products. ReadMe emphasizes interactive and structured content, helping developers explore APIs and integrate them efficiently.
While ReadMe excels in its domain, it is narrowly focused on developer documentation. It is not suitable for internal knowledge management, HR processes, QA workflows, or non-technical content. Organizations looking for a broader KM solution should consider complementary tools for internal or enterprise-wide knowledge sharing.
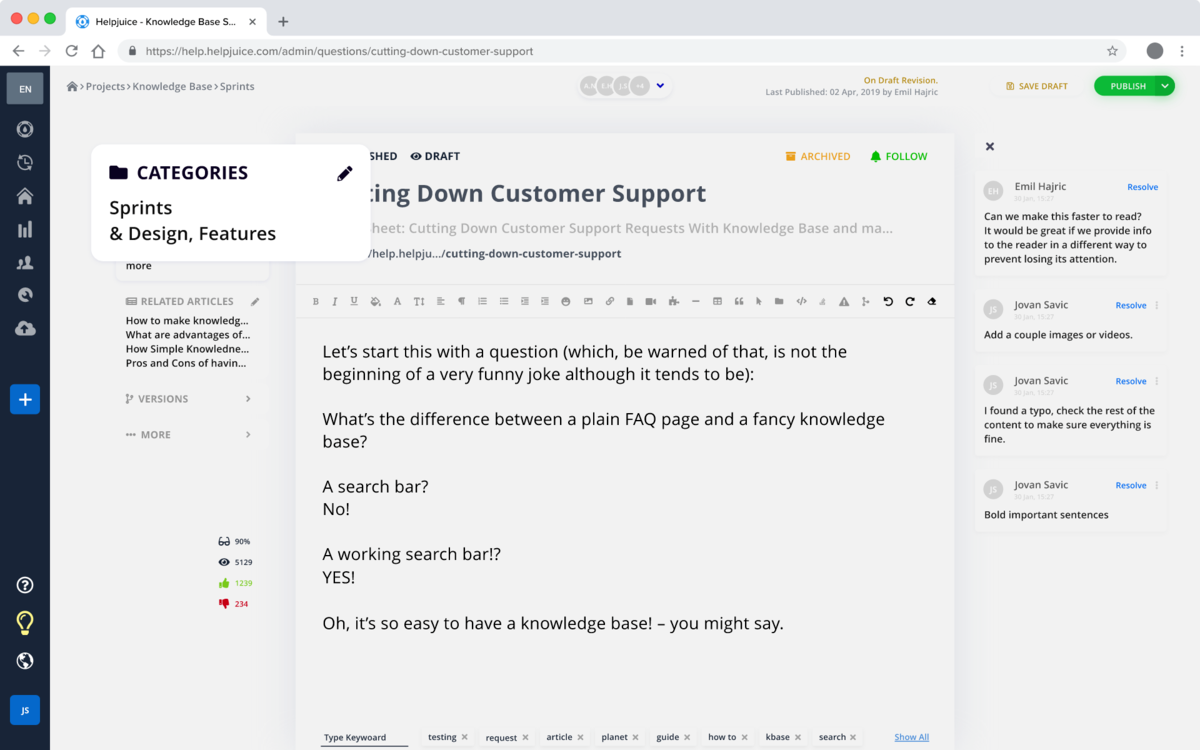
Helpjuice is a knowledge base platform designed to make creating, organizing, and accessing information simple and efficient. Its primary focus is on ease of use and powerful search capabilities, enabling teams to quickly find the answers they need. Helpjuice is ideal for customer support teams, internal documentation, and organizations that want a clean, searchable knowledge repository without heavy technical overhead.
The platform supports structured article management, categories, tags, and versioning, making it easy to maintain an organized and up-to-date knowledge base. Its search engine is particularly strong, allowing employees or customers to locate relevant information quickly. Helpjuice is a solid choice for teams seeking fast adoption, minimal learning curves, and effective knowledge discoverability.
While it excels at internal and external knowledge sharing, it is primarily designed for documentation purposes and lacks advanced social or collaboration features found in more interactive platforms.
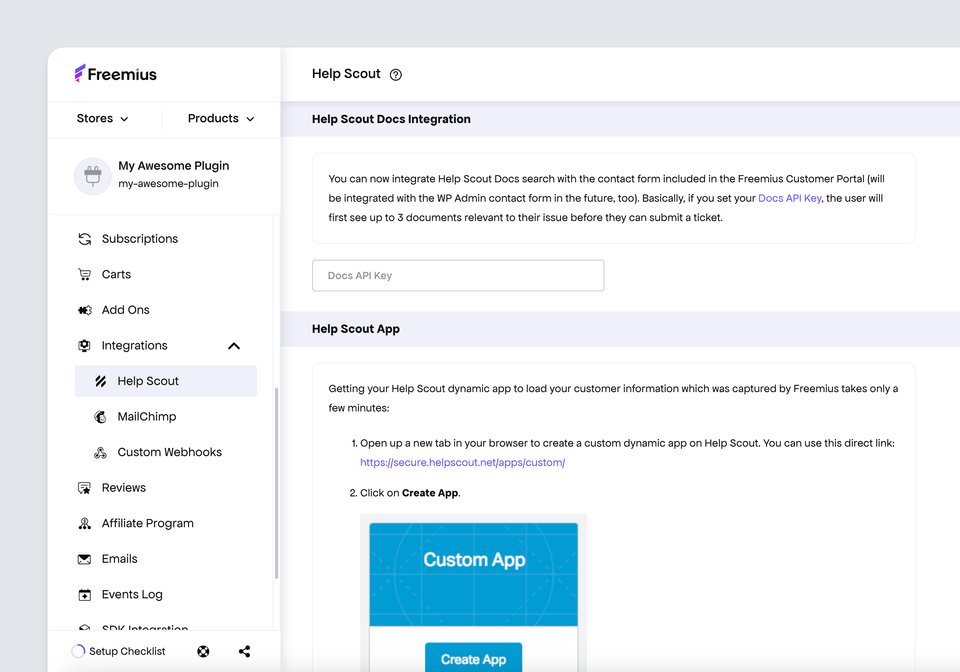
Help Scout Docs is a public-facing knowledge base designed to help small-to-medium support teams provide self-service documentation for customers. Its core goal is to reduce repetitive support inquiries by making answers easily accessible online. Docs integrates seamlessly with Help Scout’s email-based ticketing system, allowing support teams to link articles to tickets and provide contextual guidance to customers.
The platform is ideal for teams looking for a clean, simple, and easy-to-manage documentation solution without the complexity of full-scale internal knowledge management platforms. Its straightforward interface encourages fast setup and adoption, making it especially useful for startups and small businesses.
While excellent for customer-facing knowledge, Help Scout Docs is not designed as a comprehensive internal knowledge management tool, lacking advanced collaboration, workflow, or governance features for internal teams.
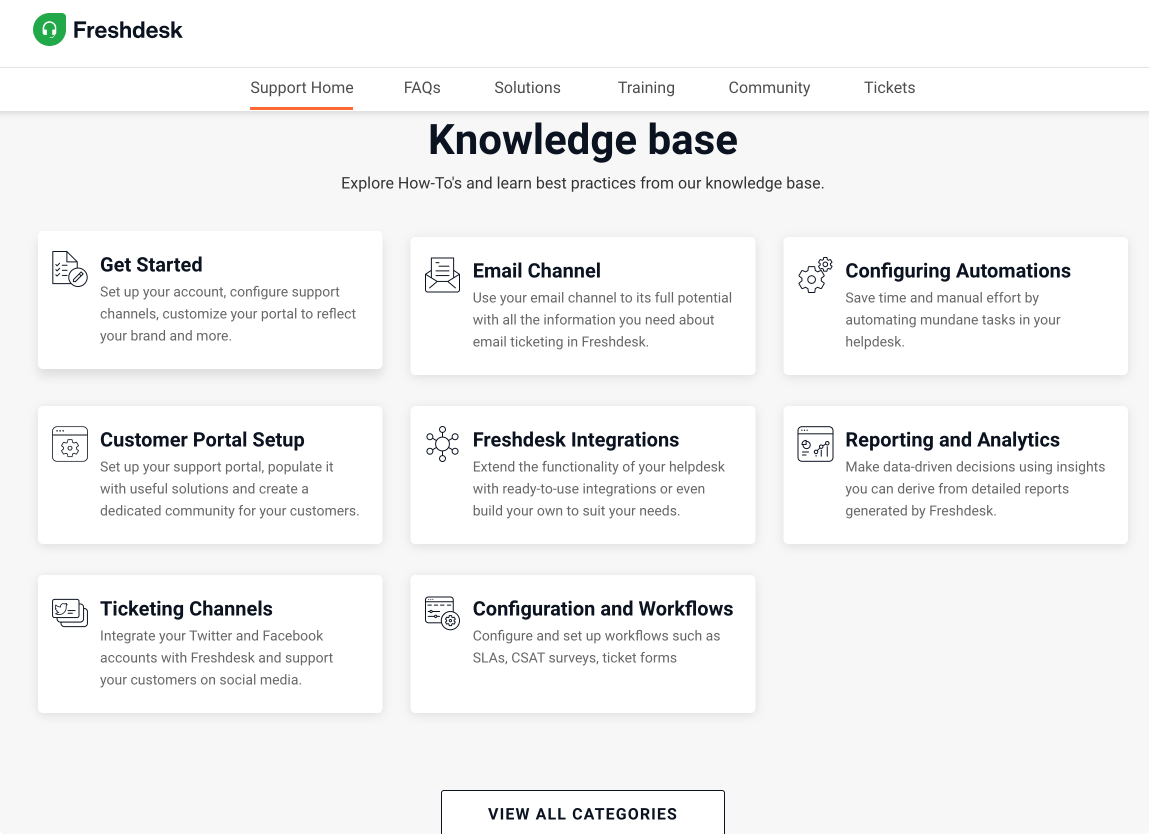
Freshdesk and Freshservice Knowledge provide integrated knowledge management for support and IT teams, embedding articles directly into ticketing and IT service management (ITSM) workflows. These platforms enable organizations to maintain accurate, up-to-date knowledge for both agents and customers, automate content suggestions, and reduce repetitive inquiries.
The knowledge base is tightly integrated with Freshworks’ support and ITSM suite, allowing articles to appear contextually alongside tickets, service requests, and incident reports. This makes it especially useful for customer support teams, IT departments, and service desk environments that need a knowledge system embedded within their operational workflows.
While effective for support-focused knowledge, Freshdesk/Freshservice Knowledge lacks flexibility for intranet-style content, broader internal collaboration, or advanced enterprise KM scenarios. Its focus is on actionable, ticket-linked knowledge rather than social or community-driven engagement.

ServiceNow Knowledge is a robust knowledge management platform built for enterprise IT and service management. It is designed to support large organizations that require governed, scalable, and process-driven knowledge systems. The platform integrates tightly with ITSM workflows, allowing knowledge articles to be linked with tickets, approvals, SLAs, and other operational processes.
ServiceNow Knowledge is ideal for IT teams, service desks, and large-scale enterprise operations that need structured, reliable, and auditable knowledge management. Its strength lies in enforcing workflows, compliance, and operational governance while ensuring that critical knowledge is accessible and actionable for teams handling complex IT and service tasks.
While extremely powerful, ServiceNow Knowledge is complex and resource-intensive, making it less suitable for small teams or organizations seeking lightweight, flexible KM tools.
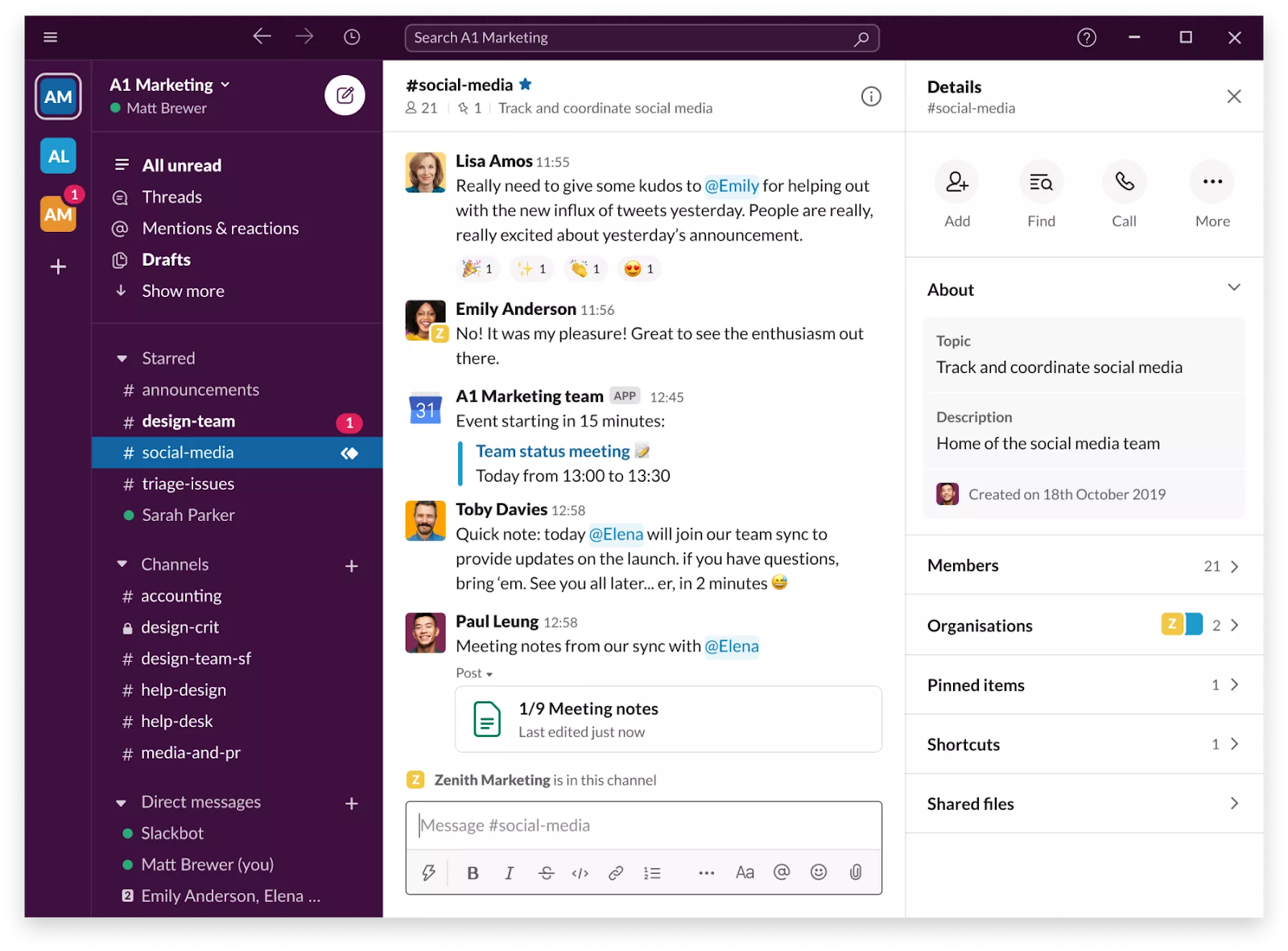
Slack, combined with Slack Huddles (formerly Slack Atlas), serves as a lightweight, informal knowledge management environment. Teams can share information through channels, threads, and direct messages, while Huddles introduces AI-powered search and discovery across Slack and connected tools, helping employees locate knowledge buried in conversations.
Slack is particularly effective for real-time collaboration and ad-hoc knowledge sharing, capturing tacit knowledge through discussions and group problem-solving. While not a structured knowledge base, Slack channels act as living repositories where teams document decisions, share updates, and collaboratively solve problems.
By integrating Huddles, Slack enhances searchability and knowledge retrieval, bridging the gap between informal communication and actionable insights. This makes it useful for teams that want lightweight, conversation-driven knowledge capture without deploying a full KM platform.
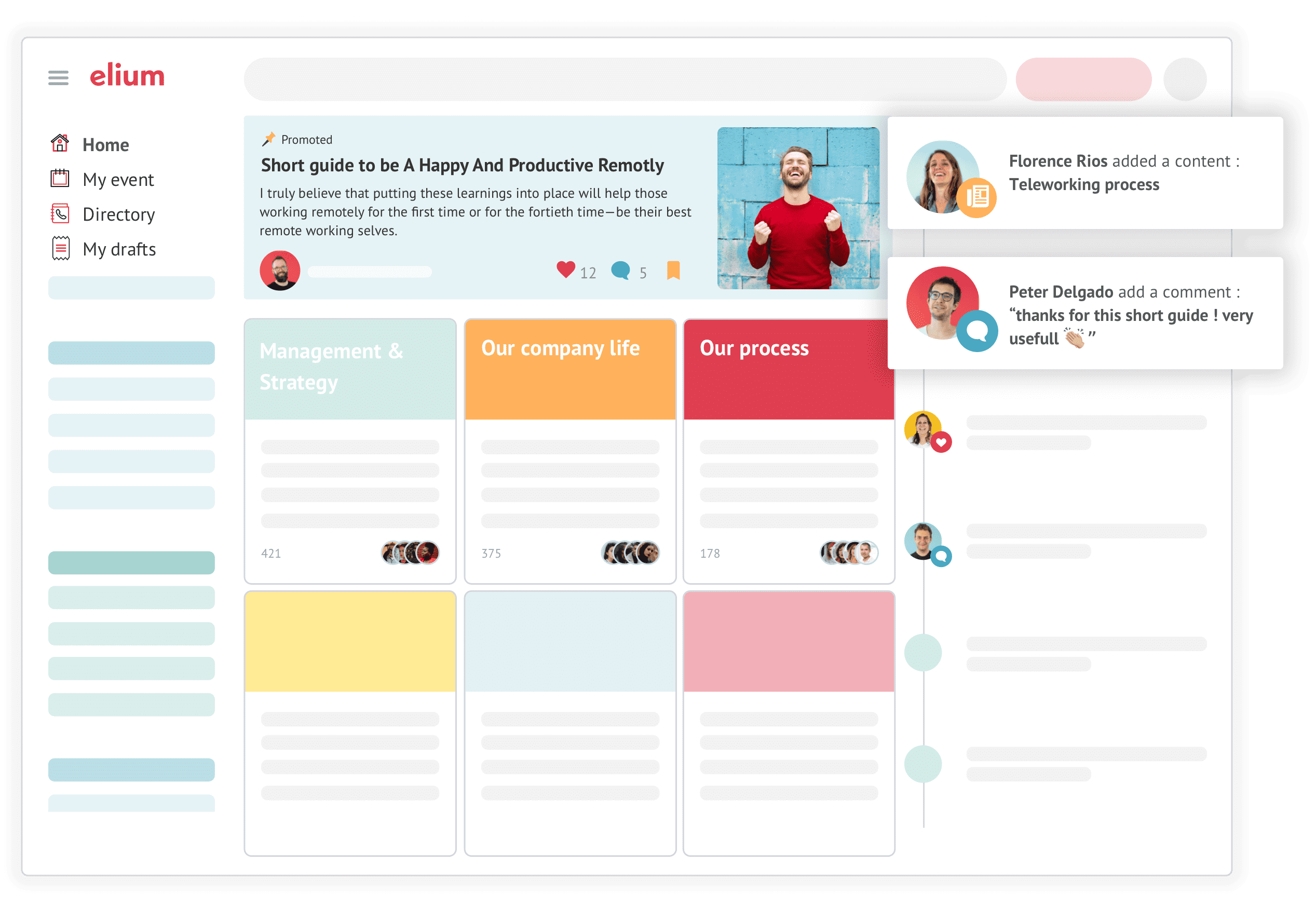
Elium is a knowledge management platform tailored for European organizations, emphasizing knowledge discoverability, collaboration, and analytics. It helps teams capture internal expertise, centralize information, and make it easily searchable across the organization. Elium is designed to enhance internal knowledge sharing while supporting compliance with European data privacy and security standards.
The platform is particularly effective for medium-to-large enterprises that want to combine structured knowledge management with collaboration-driven workflows. Its analytics features allow organizations to track knowledge usage, identify expertise, and continuously improve content relevance. By focusing on discoverability and engagement, Elium ensures that employees can quickly locate information and tap into collective expertise.
While it offers robust KM capabilities, Elium’s regional focus means some features or integrations available in US-based platforms may be limited, making it particularly suitable for European teams prioritizing local compliance and collaboration.
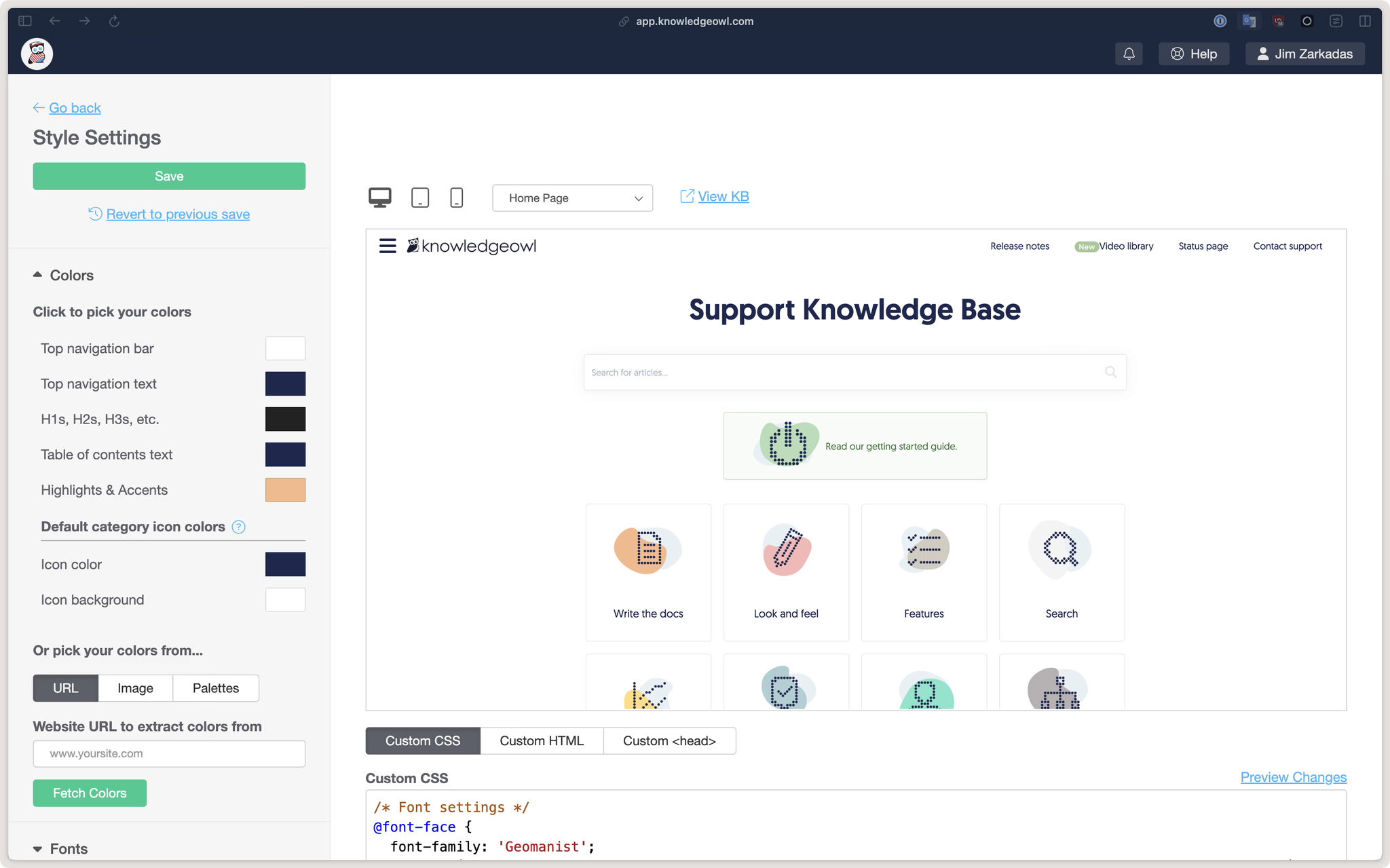
KnowledgeOwl is a structured documentation platform designed for organizations that need manuals, technical content, or compliance documentation. It provides a clear content hierarchy, version control, and both private and public access options, making it ideal for companies that require well-organized, policy-driven knowledge management.
The platform excels at authoring and publishing content that is precise, searchable, and accessible to the intended audience. KnowledgeOwl is particularly useful for regulatory-heavy industries, product documentation teams, and compliance-focused organizations, where clarity and structure are essential.
While KnowledgeOwl is strong in document authoring and content organization, its interface leans toward functionality rather than modern design or collaborative features. Organizations may need to combine it with other tools for broader internal collaboration or social knowledge sharing.
Zoho Wiki and Zoho Desk Docs are knowledge base modules integrated within the Zoho ecosystem, designed for small to medium-sized businesses seeking a cost-effective way to manage internal and customer-facing knowledge. These platforms allow teams to create, organize, and share documentation while leveraging the broader Zoho suite, including CRM, support, and project management tools.
The tools are ideal for organizations looking for affordable, easy-to-use KB solutions that integrate directly into their existing Zoho workflows. While they may not have all the advanced features of specialized KM platforms, they provide sufficient capabilities for internal wikis, FAQs, and support documentation.
Zoho Wiki and Desk Docs are particularly effective for teams already using Zoho products, offering a seamless experience across CRM, customer support, and collaboration tools. However, they may lack the depth and customization options found in enterprise-grade KM solutions.
Quip is a collaborative document and spreadsheet platform tightly integrated with Salesforce, allowing teams to create, edit, and share content directly within the CRM environment. It combines docs, spreadsheets, and chat functionality in a single interface, enabling real-time collaboration while keeping context with Salesforce data and workflows.
Quip is particularly well-suited for Salesforce-heavy organizations where teams need to link documentation, reports, and project plans directly to CRM records. It supports collaboration across departments, ensuring that documents, discussions, and data remain synchronized within Salesforce, improving efficiency and reducing context switching.
While it is a powerful collaboration tool, Quip’s full value is realized only for teams using Salesforce extensively, and it may be less compelling for organizations outside the Salesforce ecosystem.
Bit.ai is a modern content collaboration platform designed to help teams create, organize, and share knowledge in structured folders. It supports rich media embedding—images, videos, spreadsheets, and interactive content—making it ideal for teams that need flexible, visually rich documentation.
The platform is particularly suitable for startups and mid-sized teams seeking agile, easy-to-use knowledge management without the overhead of enterprise-grade governance. Bit.ai workspaces allow teams to centralize project documentation, guides, and collaborative content, while maintaining a clear folder structure for discoverability.
While Bit.ai excels at modern content creation and collaboration, it is not a full enterprise KM solution. Features such as advanced access controls, compliance governance, or structured workflows are limited, making it less suited for large, heavily regulated organizations.
HelpCrunch Docs is a lightweight knowledge base platform designed for startups and small businesses. It integrates seamlessly with HelpCrunch’s chat and email support tools, enabling teams to manage support content and deliver help efficiently.
The platform is ideal for organizations looking to reduce repetitive support inquiries by providing clear, searchable documentation to both customers and internal teams. Its simplicity and ease of setup make it suitable for fast-moving startups that need a functional KB without complex configuration.
While HelpCrunch Docs is effective for basic support documentation, it lacks advanced search capabilities, detailed governance, and enterprise-scale features, which may limit usability as knowledge bases grow in size and complexity.

LivePro is an enterprise-focused knowledge management platform designed for large support teams and contact centers. It provides guided help, structured knowledge delivery, and analytics to ensure that agents have the right information at the right time during customer interactions.
The platform is ideal for organizations that require highly organized support knowledge, enabling agents to follow recommended steps, access contextually relevant articles, and maintain consistency across service interactions. LivePro also includes analytics to track knowledge usage, content effectiveness, and agent performance, helping optimize both customer support and internal knowledge workflows.
While highly capable, LivePro involves complex setup, customization, and procurement processes, making it better suited for large enterprises with dedicated KM or support operations teams.
Featurebase represents a new generation of lightweight, modern knowledge management tools, designed for small teams, startups, or organizations experimenting with KM. These platforms emphasize simplicity, semantic search, and fast deployment, enabling teams to capture and find knowledge quickly without heavy overhead.
They are particularly well-suited for fast-moving organizations that need cost-effective solutions with transparent pricing, allowing teams to start building internal knowledge bases without large upfront investments. The platforms often include intuitive interfaces, quick content creation, and lightweight collaboration features, making them accessible for teams without dedicated KM administrators.
While Featurebase and similar tools provide a fast, flexible entry point into KM, they usually lack advanced governance, enterprise-level security, or integration capabilities, which can be a limitation for larger organizations or long-term KM strategies.
Stack Overflow for Teams is a Q&A knowledge management platform tailored for software engineering and technical teams. It allows engineers to ask, answer, and search for technical solutions in a familiar, developer-friendly format. The platform encourages knowledge capture in real time, making it easier for teams to share expertise, reduce repeated troubleshooting, and maintain a living knowledge base of technical solutions.
For larger organizations with data control or regulatory requirements, Stack Overflow Enterprise offers an on-premises deployment, providing the same Q&A experience while keeping sensitive technical knowledge within corporate infrastructure. This is ideal for large engineering teams or enterprises requiring strict data governance.
While highly effective for technical knowledge, Stack Overflow is not designed for HR, policy, or broader corporate knowledge, and its value is strongest in developer-centric environments.
Read the Docs, often paired with Sphinx, is an open-source platform for versioned, static documentation, primarily targeting developers, technical teams, and open-source projects. It allows teams to write, build, and host documentation in a structured format, providing full control over content, versioning, and deployment.
The platform is ideal for organizations or communities that want self-hosted, versioned documentation without relying on proprietary SaaS tools. Sphinx enables custom formatting, cross-references, and integration with code repositories, making it particularly suited for technical guides, APIs, and developer manuals.
While free and highly customizable, it requires engineering resources for setup, hosting, and maintenance, and is not intended as a full enterprise intranet or knowledge-sharing platform for general business teams.
| # | Product | Best For / Focus | Key Pros | Key Cons | Pricing |
| 1 | eXo Platform | All-in-one Digital Workplace & Internal Knowledge | Integrated wiki, KB, intranet & social collaboration; AI expertise locator; strong governance & gamification; flexible on-prem/cloud deployment. | Enterprise-focused; heavier implementation; primarily internal; enterprise-level pricing. | Quote / Enterprise |
| 2 | Confluence (Atlassian) | Structured Corporate Wikis & Documentation | Highly scalable with page hierarchies; deep Atlassian (Jira) integration; extensive templates & marketplace; enterprise-ready permissions. | Interface can feel clunky; overkill for small teams; risk of content accumulation without governance. | Free → $6+/user/mo |
| 3 | Notion | Flexible, Customizable All-in-One Workspace | Extremely flexible for notes, wikis, databases; beautiful and intuitive UI; free plan; vibrant template ecosystem. | Can become messy without governance; search can weaken at scale; moderate collaboration features. | Freemium; $8+/user/mo |
| 4 | Guru | Verified, In-Workflow Knowledge (Sales, Support) | Knowledge "Cards" embedded in Slack, Teams, CRM; AI-powered verification; fast lookup reduces context switching. | Not for long-form documentation; limited customization. | $14+/user/mo |
| 5 | Microsoft SharePoint | Enterprise Document Management & Intranet (Microsoft 365) | Strong governance, security & compliance; deep Office 365/Teams integration; robust document management & customizable workflows. | Complex setup; steep learning curve; heavy UX for KM-focused workflows. | Microsoft 365 plan ($5+/user/mo) |
| 6 | Bitrix24 | All-in-One Collaboration Suite with KB | Broad toolset (chat, tasks, CRM, KM); budget-friendly with free tier; accessible setup. | Crowded interface; knowledge base is basic; learning curve for full suite. | Free → Paid tiers |
| 7 | Bloomfire | Social KM & Q&A for Engagement | User-friendly, social feed interface; AI-powered search; strong analytics; encourages Q&A and learning culture. | Less structured for long docs; enterprise pricing; focus on engagement over governance. | $25+/user/mo |
| 8 | Document360 | Structured Internal & Customer-Facing KBs | Excellent structured articles & versioning; role-based permissions; professional documentation for products/customers. | Minimal social/internal collaboration; focused on KBs. | $149+/project/mo |
| 9 | Zendesk Guide / Help Center | Customer Support KB (Internal & External) | Optimized for support workflows; tight ticket integration; structured and searchable content. | Best with Zendesk Suite; add-ons increase cost; primarily support-focused. | Per agent / Suite pricing |
| 10 | Slab / Slite | Fast Internal Team Wiki & Runbooks | Clean, intuitive UX; fast search; Slack/Google Drive integrations; lightweight adoption. | Less flexible than Notion; smaller ecosystem; mainly for internal knowledge. | Free → $8.75+/user/mo |
| 11 | Jive (Aurea) | Enterprise Social Collaboration & KM | Combines activity streams, communities & KM; captures tacit knowledge; scalable; governance & analytics. | Enterprise-focused; complex implementation; heavier interface. | Enterprise / Quote |
| 12 | Igloo | Digital Workplace Intranet & Community Building | Focus on internal communities & culture; intranet capabilities; user-friendly interface; centralized knowledge & collaboration. | Less specialized for KM; customization may require effort. | Quote-based |
| 13 | Tettra | Slack-Integrated Internal Q&A & Wiki | Quick setup; simple Q&A workflow; deep Slack & Google Workspace integration. | Limited public KB support; basic governance; not for complex documentation. | Paid per user |
| 14 | ReadMe | Interactive Developer Portals & API Docs | Developer-first with API consoles & interactive examples; versioned docs; improves developer onboarding & support. | Narrow focus on external developer docs; not internal KM. | Tiered / Vendor-specific |
| 15 | Helpjuice | Easy-to-Use KB with Powerful Search | Simple, intuitive interface; powerful search; structured knowledge management; quick setup. | Focused on KBs; limited collaboration features; enterprise integrations may be limited. | Tiered plans |
| 16 | Help Scout Docs | Simple Customer-Facing KB for SMBs | Easy to set up; integrates with Help Scout email/tickets; clean interface; reduces support load. | Not suitable for full internal KM; primarily public-facing; limited advanced features. | Included with Help Scout plan |
| 17 | Freshdesk / Freshservice KB | Support & ITSM-Integrated Knowledge | Automation & ticket/ITSM integration; suggests articles to agents; ensures up-to-date knowledge. | Limited intranet flexibility; support-focused; less suited for general-purpose KM. | Bundled in Freshworks plans |
| 18 | ServiceNow Knowledge | Enterprise IT/Service Management (ITSM) KM | Scales for large enterprises; deep ITSM workflow integration (SLAs, approvals); governed and auditable. | Complex, costly implementation; heavyweight for smaller teams; less flexible. | Enterprise / Quote |
| 19 | Slack (Huddles & Channels) | Informal, Real-Time Knowledge Sharing | Real-time collaboration in channels; AI-powered search; captures tacit knowledge; lightweight adoption. | Informal structure; not a formal KB; knowledge can get buried; best as complement to structured KM. | Freemium; $7.25+/user/mo |
| 20 | Elium | European Enterprise KM & Collaboration | Knowledge discoverability & analytics; collaboration-focused; compliant with European data standards. | Regional focus may limit feature parity; not public-facing; requires training. | Quote-based |
| 21 | KnowledgeOwl | Manuals, Compliance & Technical Documentation | Strong structured authoring & hierarchy; private/public portals; version control; documentation-heavy workflows. | Functional but less modern UI; limited collaboration; niche-focused. | Tiered plans |
| 22 | Zoho Wiki / Desk Docs | SMBs in the Zoho Ecosystem | Affordable; integrated with Zoho CRM, Desk, etc.; simple setup; sufficient for SMB wikis and FAQs. | Lighter feature set; limited scalability; best for existing Zoho users. | Included in Zoho plan |
| 23 | Quip (Salesforce) | Salesforce-Integrated Collaborative Docs | Seamless Salesforce integration; combines docs, spreadsheets & chat; real-time collaboration in CRM context. | Salesforce-centric; not a full KM platform; limited value outside ecosystem. | Included in Salesforce bundles |
| 24 | Bit.ai | Modern Team Content Collaboration | Easy document creation with rich media embedding; structured folders; intuitive and modern interface. | Limited enterprise governance; not full KM; scaling limitations. | Free → Paid tiers |
| 25 | HelpCrunch Docs | Simple Startup KB with Chat/Email Support | Easy setup; integrated with HelpCrunch support tools; startup-friendly; reduces support load. | Limited search/governance; primarily customer-facing. | Included with HelpCrunch plan |
| 26 | LivePro | Contact Center & Enterprise Support KM | Guided help for agents; enterprise analytics; ensures consistent service; enterprise-ready. | Heavy setup & customization; procurement-intensive; not lightweight. | Quote-based |
| 27 | Featurebase / New Entrants | Modern, Lightweight Startup KM | Simple, intuitive setup; semantic search; cost-effective & transparent pricing; modern UI/UX. | Limited governance; uncertain long-term support; not enterprise-grade. | Contact vendor |
| 28 | Stack Overflow for Teams | Developer Q&A & Technical Knowledge | Fast, targeted answers; developer-centric UX; powerful search; on-premises option (Enterprise). | Not suited for HR/policy/general knowledge; license costs; niche focus. | Tiered per-seat pricing |
| 29 | Stack Overflow Enterprise | On-Premises Developer Q&A | Enterprise control; familiar Q&A model; scalable for large engineering teams. | License cost; setup effort; limited non-technical coverage. | Quote-based |
| 30 | Read the Docs / Sphinx | Open-Source Developer Documentation | Free & versioned; highly customizable; full control over hosting & structure. | Requires DevOps/engineering; static content; not full enterprise intranet. | Free / Paid hosting |
Knowledge is one of the most valuable assets of any organization. But in today’s fast-paced, hybrid work environments, simply having information isn’t enough. Teams need the right Knowledge Management (KM) software to capture, organize, share, and retrieve knowledge efficiently. The right tool can boost productivity, improve onboarding, accelerate problem-solving, and even enhance customer experience. Choosing it, however, requires more than comparing features—it’s about matching the software to your team’s workflow, culture, and long-term goals.
This guide will help you evaluate Knowledge Management tools effectively, provide a detailed feature checklist, and offer practical recommendations to ensure adoption and impact.
When evaluating Knowledge Management software, start with the fundamental capabilities every modern tool should provide:
Modern Knowledge Management platforms increasingly integrate AI to reduce friction and improve productivity:
AI-powered features can dramatically reduce time spent hunting for information, but only if implemented thoughtfully.
A Knowledge Management platform doesn’t exist in a vacuum. Consider how it connects with your existing systems:
Integration readiness often determines whether a Knowledge Management tool will be adopted or ignored.
Enterprise organizations require more than just search—they need control:
Even the best features are useless if employees don’t use the system:
Finally, evaluate the business and operational model:
If your priority is a fully integrated digital workplace with KM, platforms like eXo Platform or SharePoint cover most of these boxes—they combine intranet, collaboration, knowledge governance, and on-prem/cloud deployment options.
Choosing the right Knowledge Management tool is as much about your team’s personality as it is about features:
The best KM software is the one your team will actually use. Start by identifying your biggest pain point: finding information, keeping it updated, or getting people to share knowledge in the first place. This answer will guide your decision.
Choosing the right Knowledge Management software is far more than a technical decision — it’s a strategic investment in how your organization learns, collaborates, and evolves. At its best, a Knowledge Management system becomes the beating heart of your company’s intelligence, empowering every employee to contribute, discover, and apply knowledge effortlessly.
In the modern workplace, knowledge moves fast. Teams generate new insights every day — from customer conversations to project retrospectives — but without the right system, that wisdom often disappears into silos, emails, or forgotten folders. The true purpose of a Knowledge Management solution is to capture that collective intelligence, refine it, and make it instantly accessible where and when it’s needed most.
A strong Knowledge Management platform doesn’t just organize information; it cultivates a culture of sharing and continuous improvement. It encourages people to document their experiences, share lessons learned, and build on one another’s expertise. Over time, this turns knowledge into a renewable, compounding asset — one that strengthens performance, accelerates onboarding, and fuels innovation.
The most successful organizations don’t treat KM as an isolated project but as a strategic pillar of their digital workplace. They integrate it into their daily workflows, link it to communication and collaboration tools, and assign clear ownership and governance. When done right, Knowledge Management becomes invisible — seamlessly embedded in the way people work, connect, and learn every day.
At the end of the day, the goal is simple yet transformative:
to make knowledge flow freely across teams, empower people to do their best work, and ensure that no expertise is ever lost when someone closes their laptop for the day.
If your organization is ready to take that step — to connect your people, culture, and knowledge in one unified digital workplace — we at eXo Platform would be glad to help you make it happen.
👉 Contact us to explore how an integrated digital workplace can turn your company’s knowledge into its most powerful advantage.

eXo Platform : The Open-Source
Digital Workplace Platform
Download the eXo Platform Datasheet and discover all the features and benefits


Download the eXo Platform Datasheet and discover all the features and benefits
You will find here Frequently Asked Questions about Knwoledge Management Software (KMS) with all the answers in one place.
Knowledge Management Software (KMS) is a technology solution that helps organizations capture, organize, share, and make the most of their collective knowledge. It acts like a corporate brain—a centralized hub where employees can access company policies, project documentation, best practices, technical specifications, FAQs, and other critical information.
➝ See the full definition of Knowledge Management Software (KMS).
Knowledge Management Software (KMS) comes in many forms, each tailored to different needs, audiences, and organizational goals. No single tool fits every use case—some focus on customer-facing knowledge, others on internal collaboration or AI-powered discovery.
Below is a guide to the main types of Knowledge Management Software and what makes each one unique.
➝ Find out the different types of Knowledge Management Software.
Knowledge Management Software (KMS) is more than just a digital repository—it’s your organization’s searchable brain. It centralizes policies, how-to guides, troubleshooting steps, customer answers, R&D notes, and “tribal knowledge” (the know-how that lives in employees’ heads) all in one place. A robust KM system transforms scattered information into actionable knowledge, helping teams work smarter, faster, and more collaboratively.
Here’s why Knowledge Management Software matters:
Knowledge Management Software (KMS) delivers measurable, organization-wide impact. Beyond simply storing information, a well-implemented KMS improves productivity, speeds up problem-solving, preserves expertise, and fosters a more connected and innovative workplace.
Let’s explore the key benefits and outcomes businesses can expect when adopting a robust knowledge management strategy.
➝ Find out the Key Benefits of Knowledge Management Software.
Knowledge is one of the most valuable assets of any organization. But in today’s fast-paced, hybrid work environments, simply having information isn’t enough. Teams need the right Knowledge Management (KM) software to capture, organize, share, and retrieve knowledge efficiently. The right tool can boost productivity, improve onboarding, accelerate problem-solving, and even enhance customer experience. Choosing it, however, requires more than comparing features—it’s about matching the software to your team’s workflow, culture, and long-term goals.
This guide will help you evaluate Knowledge Management tools effectively, provide a detailed feature checklist, and offer practical recommendations to ensure adoption and impact.
➝ Find out the best way How to Choose the Right Knowledge Management Software.
( Your e-mail address will not be published)
I am a Digital Marketing specialist specialized in SEO at eXo Platform. Passionate about new technologies and Digital Marketing. With 10 years' experience, I support companies in their digital communication strategies and implement the tools necessary for their success. My approach combines the use of different traffic acquisition levers and an optimization of the user experience to convert visitors into customers. After various digital experiences in communication agencies as well as in B2B company, I have a wide range of skills and I am able to manage the digital marketing strategy of small and medium-sized companies.